T-bet upregulation and subsequent interleukin 12 stimulation are essential for induction of Th1 mediated immunopathology in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 15306590
- PMCID: PMC1774174
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.024190
T-bet upregulation and subsequent interleukin 12 stimulation are essential for induction of Th1 mediated immunopathology in Crohn's disease
Erratum in
- Gut. 2004 Nov;53(11):1722
Abstract
Background and aims: Many lines of evidence suggest that T helper cell type 1 (Th1) immune responses predominate in Crohn's disease (CD). Recently, a novel transcription factor T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet) has been reported as the master regulator of Th1 development. This study was designed to investigate the role of T-bet and proinflammatory cytokines in Th1 mediated immunopathology in CD.
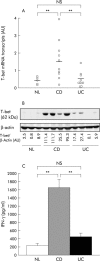
Materials: CD4+ lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMCs) were isolated from surgically resected specimens (CD, n = 10; ulcerative colitis (UC), n = 10; normal controls (NL), n = 5).
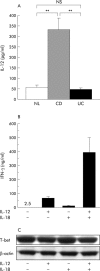
Methods: (1) T-bet expression of CD4+ LPMCs was examined by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. (2) T-bet expression of LPMCs stimulated by interleukin (IL)-12/IL-18 was analysed by western blotting. (3) Interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) production and T-bet expression of CD4+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were examined with or without stimulation by anti-CD3/CD28 monoclonal antibodies and/or IL-12.
Results: (1) T-bet expression of CD4+ LPMCs was increased in CD compared with UC and NL. (2) Synergistically, augmentation of IFN-gamma production by IL-12/IL-18 was independent of T-bet expression in LPMCs. (3) T-bet was induced by T cell receptor stimulation in CD4+ PBMCs. T-bet induction correlated with IFN-gamma production and with augmentation of surface expressed IL-12 receptor beta2.
Conclusions: T-bet induction by antigenic stimulation and subsequent stimulation by macrophage derived IL-12/IL-18 are important for establishing Th1 mediated immunopathology in CD.
Figures
References
-
- Neurath MF, Finotto S, Glimcher LH. The role of Th1/Th2 polarization in mucosal immunity. Nat Med 2002;8:567–73. - PubMed
-
- Fiocchi C . Inflammatory bowel disease: etiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 1998;115:182–205. - PubMed
-
- Kanai T , Watanabe M, Okazawa A, et al. Interleukin 18 is a potent proliferative factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2000;119:1514–23. - PubMed
-
- Fuss IJ, Neurath M, Boirivant M, et al. Disparate CD4+ lamina propria (LP) lymphokine secretion profiles in inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn’s disease LP cells manifest increased secretion of IFN-gamma, whereas ulcerative colitis LP cells manifest increased secretion of IL-5. J Immunol 1996;157:1261–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
