Sustained virological response in hepatitis C virus type 1b infected patients is predicted by the number of mutations within the NS5A-ISDR: a meta-analysis focused on geographical differences
- PMID: 15306598
- PMCID: PMC1774214
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.031336
Sustained virological response in hepatitis C virus type 1b infected patients is predicted by the number of mutations within the NS5A-ISDR: a meta-analysis focused on geographical differences
Abstract
Background and aims: There is growing evidence that the response of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1b infected patients towards interferon (IFN) therapy is influenced by the number of mutations within the carboxy terminal region of the NS5A gene, the interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR).
Patients and methods: In order to attain better insight into this correlation, a file comprising published data on ISDR strains from 1230 HCV genotype 1b infected patients, mainly from Japan and Europe, was constructed and analysed by logistic regression. Sustained virological response (SVR) was defined as negative HCV RNA six months after treatment.
Results: The distribution of wild-, intermediate-, and mutant-type ISDR sequences differed significantly between Japanese (n = 655) (44.1%, 37.6%, and 18.3%) and European patients (n = 525) (24.8%, 63.4%, and 11.8%; p<0.001). There was a significant positive correlation between the number of ISDR mutations and SVR rate, irrespective of geographical region. The likelihood of SVR with each additional mutation within the ISDR was considerably more pronounced in Japanese compared with European patients (odds ratios 1.82 v 1.39; p<0.001). Pretreatment viraemia of <6.6 log copies/ml and ISDR mutant-type infection was associated with an SVR rate of 97.1% in Japanese patients but only 52.5% in European patients. Pretreatment viraemia was a stronger predictor of SVR than ISDR mutation number in Japanese patients whereas in European patients both parameters had similar predictive power.
Conclusion: These data support the concept that mutant-type ISDR strains may represent a subtype within genotype 1b with a more favourable response towards IFN therapy.
Figures


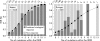



Similar articles
-
A mutation in the interferon sensitivity-determining region is associated with responsiveness to interferon-ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis patients infected with a Japan-specific subtype of hepatitis C virus genotype 1B.J Med Virol. 2007 Jan;79(1):35-40. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20766. J Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17133546
-
Viral decline over 48h and HCV amino acid mutations are related to efficacy of PEG-IFN/ribavirin.Hepatogastroenterology. 2012 May;59(115):794-9. doi: 10.5754/hge11570. Hepatogastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22020909
-
NS5A(ISDR-V3) region genetic variability of Tunisian HCV-1b strains: Correlation with the response to the combined interferon/ribavirin therapy.J Med Virol. 2009 Dec;81(12):2021-8. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21641. J Med Virol. 2009. PMID: 19856481
-
[Interferon resistance and ISDR (interferon sensitivity determining region)].Nihon Rinsho. 2006 Jul;64(7):1249-53. Nihon Rinsho. 2006. PMID: 16838640 Review. Japanese.
-
[Effects of hepatitis C virus proteins on the interferon-stimulated signal transduction].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Jul;59(7):1271-6. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11494536 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Prospects for personalizing antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus with pharmacogenetics.Genome Med. 2011 Feb 8;3(2):8. doi: 10.1186/gm222. Genome Med. 2011. PMID: 21345258 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the IL28B and sustained virologic response of patients with chronic hepatitis C to PEG-interferon/ribavirin therapy: A meta-analysis: Meta-analysis of IL28B.Hepat Mon. 2011 Mar;11(3):163-72. Hepat Mon. 2011. PMID: 22087138 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of substitutions at amino acid 70 in hepatitis C virus genotype 1b.Virol J. 2014 Aug 15;11:148. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-148. Virol J. 2014. PMID: 25128407 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of IL-6 and CCL5 (RANTES) in human respiratory epithelial (A549) cells by clinical isolates of respiratory syncytial virus is strain specific.Virol J. 2012 Sep 10;9:190. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-190. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22962966 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic response of wild and mutant core codon 70 strains of HCV genotype 1b to pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin therapy.Virol J. 2015 Dec 18;12:220. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0451-9. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 26684004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinot-Peignoux M , Marcellin P, Pouteau M, et al. Pretreatment serum hepatitis C virus RNA levels and hepatitis C virus genotype are the main and independent prognostic factors of sustained response to interferon alfa therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 1995;22:1050–6. - PubMed
-
- Poynard T , Leroy V, Cohard M, et al. Meta-analysis of interferon randomized trials in the treatment of viral hepatitis C: effects of dose and duration. Hepatology 1996;24:778–89. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomized trial. Lancet 2001;358:958–65. - PubMed
-
- Fried MW, Shiffman ML, Reddy KR, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2002;347:975–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
