Differences between CD8+ T cells in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW) F1 mice and healthy (BALB/c x NZW) F1 mice may influence autoimmunity in the lupus model
- PMID: 15307181
- PMCID: PMC2291530
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200424978
Differences between CD8+ T cells in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW) F1 mice and healthy (BALB/c x NZW) F1 mice may influence autoimmunity in the lupus model
Abstract
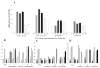
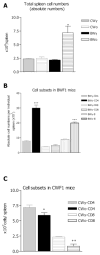
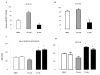
Immunization with portions of a murine antibody to DNA induced Ig peptide-reactive peripheral CD8+ inhibitory T (Ti) cells in non-autoimmune (BALB/c x NZW) F1 (CWF1) mice. Those Ti suppressed in vitro production of IgG anti-DNA by lymphocytes from MHC-matched, lupus-prone (NZB x NZW) F1 (BWF1) mice, primarily via secretion of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta). However, splenic CD8+ cells from immunized BWF1 mice failed to suppress anti-DNA. Therefore, BWF1 mice were studied for defects in peripheral CD8+ T cells. The potential to suppress autoimmunity mediated by activated CD4+ helper T and B cells in BWF1 mice was assessed. As BWF1 mice aged, peripheral CD8+ T cells expanded little; fewer than 10% displayed surface markers of activation and memory. In contrast, quantities of splenic CD4+ T and B cells increased; high proportions displayed activation/memory markers. In old compared to young BWF1 mice, splenic cell secretion of two cytokines required for generation of CD8+ T effectors, IL-2 and TGF-beta, was decreased. Immunizing BWF1 mice activated peptide-reactive CD8+ T cells, but their number was decreased compared to young BWF1 or old normal mice. While peptide-reactive splenic CD8+ T cells from immunized BWF1 mice did not survive in short-term cultures, similar CD8+ T cell lines from immunized CWF1 mice expanded and on transfer into BWF1 mice delayed autoimmunity and prolonged survival. Therefore, CD8+ T cells in old BWF1 mice are impaired in expansion, acquisition of memory, secretion of cytokine, and suppression of autoimmunity. Understanding these defects might identify targets for therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright 2004 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.
Figures



Similar articles
-
T cell determinants from autoantibodies to DNA can upregulate autoimmunity in murine systemic lupus erythematosus.J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2017-27. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2017. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7539036 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the cytokine profile of lupus-prone mice (NZB/NZW)F1 induced by Plasmodium chabaudi and their implications in the reversal of clinical symptoms.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Feb;119(2):333-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01124.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10632672 Free PMC article.
-
pConsensus peptide induces tolerogenic CD8+ T cells in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW)F1 mice by differentially regulating Foxp3 and PD1 molecules.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 15;180(4):2069-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2069. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18250412
-
Aberrant B1 cell trafficking in a murine model for lupus.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:1790-803. doi: 10.2741/2188. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127421 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of regulation of autoantibody production in lupus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1051:433-41. doi: 10.1196/annals.1361.085. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16126985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual roles of immunoregulatory cytokine TGF-beta in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity-mediated organ damage.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 1;180(3):1903-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.3.1903. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18209088 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of the parent-into-F1 model for human lupus pathogenesis: roles for cytotoxic T lymphocytes and viral pathogens.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 Sep;22(5):493-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833b0174. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20485174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon-inducible gene 202b controls CD8(+) T cell-mediated suppression in anti-DNA Ig peptide-treated (NZB × NZW) F1 lupus mice.Genes Immun. 2011 Jul;12(5):360-9. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.4. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Genes Immun. 2011. PMID: 21326316 Free PMC article.
-
Both perforin and FasL are required for optimal CD8 T cell control of autoreactive B cells and autoantibody production in parent-into-F1 lupus mice.Clin Immunol. 2018 Sep;194:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29940333 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of immune tolerance by activation of CD8+ T suppressor/regulatory cells in lupus-prone mice.Hum Immunol. 2008 Nov;69(11):790-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.08.284. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Hum Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18817829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hahn BH. Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1359–1368. - PubMed
-
- Shivakumar S, Tsokos GC, Datta SK. T cell receptor γ/δ expressing double-negative (CD4−/CD8−) and CD4+ T helper cells in humans augment the production of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies associated with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1989;143:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Filaci G, Bacilieri S, Fravega M, Monetti M, Contini P, Ghio M, et al. Impairment of CD8+ T suppressor cell function in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2001;166:6452–6457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

