A DNA vaccine producing LcrV antigen in oligomers is effective in protecting mice from lethal mucosal challenge of plague
- PMID: 15308359
- PMCID: PMC7126436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.02.036
A DNA vaccine producing LcrV antigen in oligomers is effective in protecting mice from lethal mucosal challenge of plague
Abstract
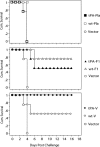
There is an urgent need to develop effective vaccines against pneumonic plague, a highly lethal and contagious disease caused by the Gram-negative bacterium Yersinia pestis. Here we demonstrate that a novel DNA vaccine expressing a modified V antigen (LcrV) of Y. pestis, with a human tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) signal sequence, elicited strong V-specific antibody responses in BALB/c mice. This tPA-V DNA vaccine protected mice from intranasal challenge with lethal doses of Y. pestis. In comparison, a DNA vaccine expressing the wild type V antigen was much less effective. Only tPA-V formed oligomers spontaneously, and elicited a higher IgG2a anti-V antibody response in immunized mice, suggesting increased TH1 type cellular immune response. Our data indicate that antigen engineering is effective in inducing high quality protective immune responses against conformationally sensitive antigens. These results support that optimized DNA vaccines have the potential to protect against bacterial pathogens than is generally recognized.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intranasal delivery of a protein subunit vaccine using a Tobacco Mosaic Virus platform protects against pneumonic plague.Vaccine. 2016 Nov 11;34(47):5768-5776. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.09.063. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27745954 Free PMC article.
-
rLVS ΔcapB/Yp F1-V single vector platform vaccine expressing Yersinia pestis F1 and LcrV antigens provides complete protection against lethal respiratory challenge with virulent plague bacilli.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2507475. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2507475. Epub 2025 May 26. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40417828 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia pestis YadC: a novel vaccine candidate against plague.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;603:400-14. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-72124-8_37. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17966436
-
Protecting against plague: towards a next-generation vaccine.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Apr;172(1):1-8. doi: 10.1111/cei.12044. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23480179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for new plague vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2009 Dec;8(12):1721-38. doi: 10.1586/erv.09.129. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2009. PMID: 19943765 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying Key Drivers of Efficient B Cell Responses: On the Role of T Help, Antigen-Organization, and Toll-like Receptor Stimulation for Generating a Neutralizing Anti-Dengue Virus Response.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;12(6):661. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12060661. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38932390 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus-mediated delivery of an anti-V antigen monoclonal antibody protects mice against a lethal Yersinia pestis challenge.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1561-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00856-08. Epub 2009 Jan 5. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19124600 Free PMC article.
-
Plague Vaccine Development: Current Research and Future Trends.Front Immunol. 2016 Dec 14;7:602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00602. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28018363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relative immunogenicity and protection potential of candidate Yersinia Pestis antigens against lethal mucosal plague challenge in Balb/C mice.Vaccine. 2008 Mar 20;26(13):1664-74. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.01.024. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18291562 Free PMC article.
-
Current challenges in the development of vaccines for pneumonic plague.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008 Mar;7(2):209-21. doi: 10.1586/14760584.7.2.209. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008. PMID: 18324890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williamson E.D., Eley S.M., Stagg A.J., Green M., Russell P., Titball R.W. A sub-unit vaccine elicits IgG in serum, spleen cell cultures and bronchial washings and protects immunized animals against pneumonic plague. Vaccine. 1997;15(10):1079–1084. - PubMed
-
- Williamson E.D., Eley S.M., Stagg A.J., Green M., Russell P., Titball R.W. A single dose sub-unit vaccine protects against pneumonic plague. Vaccine. 2001;19(4–5):566–571. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues C.G., Carneiro C.M., Barbosa C.T., Nogueira R.A. Antigen F1 from Yersinia pestis forms aqueous channels in lipid bilayer membranes. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1992;25(1):75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

