A randomised comparative study of the short term clinical and biological effects of intravenous pulse methylprednisolone and infliximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment
- PMID: 15308515
- PMCID: PMC1755125
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.012914
A randomised comparative study of the short term clinical and biological effects of intravenous pulse methylprednisolone and infliximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the short term clinical and biological effects of intravenous (i.v.) pulse methylprednisolone (MP) and infliximab (IFX) in patients with severe active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite methotrexate (MTX) treatment.
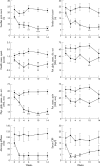
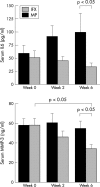
Methods: Patients with active RA despite MTX treatment were randomly allocated to receive a single i.v. infusion of MP (1 g) or three i.v. infusions of IFX (3 mg/kg) on weeks 0, 2, and 6. Patients were "blindly" evaluated for disease activity measures. Quality of life (QoL) was evaluated through the SF-36 health survey. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) titres were measured at baseline, weeks 2 and 6.
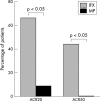
Results: Compared with baseline, significant improvement was noted in all activity measures, including serum C reactive protein (CRP) titres, in the IFX group only. At week 14, 6/9 (67%) and 4/9 (44%) IFX patients met the ACR20 and 50 response criteria, while this was the case in only 1/12 (8%) and 0/12 (0%) MP patients, respectively (p<0.05). None of the QoL scales improved with MP treatment, whereas some did so in the IFX group. Serum MMP-3 titres significantly decreased (41% drop) at week 6 in the IFX group, while no changes were seen in patients given MP.
Conclusion: This short term randomised comparative study demonstrates that TNF blockade is better than MP pulse therapy in a subset of patients with severe refractory RA, with improvement in not only clinical parameters of disease activity but also biological inflammatory indices, such as serum CRP and MMP-3 titres.
Figures
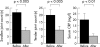
Comment in
-
Which dose regimen for glucocorticoid pulse therapy in patients with severe refractory RA?Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Jan;64(1):171-2; author reply 172. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15608329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is IV infliximab better than IV methylprednisolone for the treatment of patients with RA when methotrexate fails?Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Mar;64(3):512; author reply 512. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15708914 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

