Efficacy in CB1 receptor-mediated signal transduction
- PMID: 15308578
- PMCID: PMC1575189
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705881
Efficacy in CB1 receptor-mediated signal transduction
Abstract
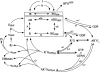
CB(1) receptor cellular signal transduction is dependent on the expression of G proteins to which the receptor couples, the potential for precoupling of particular G proteins to the receptors either by scaffolding mechanisms or colocalization in lipid raft domains, and the effector mechanisms that these transducer molecules regulate. This discourse will evaluate studies of efficacy for CB(1) receptor-Gi/o activation at the molecular level. Evidence for brain regional differences in CB(1) receptor signal transduction efficacy and agonist selectivity for G proteins will be summarized. The possibility that CB(1) receptors interact with Gs or Gq will be evaluated, and questions with regard to the constitutive activity and G protein sequestration will be posed.
Figures
References
-
- ABADJI V., LUCAS-LENARD J.M., CHIN C., KENDALL D.A. Involvement of the carboxyl terminus of the third intracellular loop of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor in constitutive activation of Gs. J. Neurochem. 1999;72:2032–2038. - PubMed
-
- ADAMS I.B., COMPTON D.R., MARTIN B.R. Assessment of anandamide interaction with the cannabinoid brain receptor: SR 141716A antagonism studies in mice and autoradiographic analysis of receptor binding in rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;284:1209–1217. - PubMed
-
- BASKFIELD C.Y., MARTIN B.R., WILEY J.L. Differential effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and methanandamide on operant behavior in CB1 knockout and wild type mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004;309:86–91. - PubMed
-
- BONHAUS D.W., CHANG L.K., KWAN J., MARTIN G.R. Dual activation and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by cannabinoid receptor agonists: evidence for agonist-specific trafficking of intracellular responses. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;287:884–888. - PubMed
-
- BOUABOULA M., PERRACHON S., MILLIGAN L., CANAT X., RINALDI-CARMONA M., PORTIER M., BARTH F., CALANDRA B., PECCEU F., LUPKER J., MAFFRAND J.P., LE FUR G., CASELLAS P. A selective inverse agonist for central cannabinoid receptor inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase activation stimulated by insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1. Evidence for a new model of receptor/ligand interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:22330–22339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

