The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility
- PMID: 15308757
- PMCID: PMC520935
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.024919
The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility
Abstract
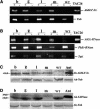
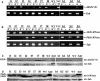
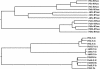
Recently, we have provided evidence that the polymorphic self-incompatibility (S) locus-encoded F-box (SLF) protein AhSLF-S(2) plays a role in mediating a selective S-RNase destruction during the self-incompatible response in Antirrhinum hispanicum. To investigate its role further, we first transformed a transformation-competent artificial chromosome clone (TAC26) containing both AhSLF-S(2) and AhS(2)-RNase into a self-incompatible (SI) line of Petunia hybrida. Molecular analyses showed that both genes are correctly expressed in pollen and pistil in four independent transgenic lines of petunia. Pollination tests indicated that all four lines became self-compatible because of the specific loss of the pollen function of SI. This alteration was transmitted stably into the T1 progeny. We then transformed AhSLF-S(2) cDNA under the control of a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) pollen-specific promoter LAT52 into the self-incompatible petunia line. Molecular studies revealed that AhSLF-S(2) is specifically expressed in pollen of five independent transgenic plants. Pollination tests showed that they also had lost the pollen function of SI. Importantly, expression of endogenous SLF or SLF-like genes was not altered in these transgenic plants. These results phenocopy a well-known phenomenon called competitive interaction whereby the presence of two different pollen S alleles within pollen leads to the breakdown of the pollen function of SI in several solanaceaous species. Furthermore, we demonstrated that AhSLF-S(2) physically interacts with PhS(3)-RNase from the P. hybrida line used for transformation. Together with the recent demonstration of PiSLF as the pollen determinant in P. inflata, these results provide direct evidence that the polymorphic SLF including AhSLF-S(2) controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility.
Figures


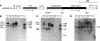



Similar articles
-
Self-incompatibility in Petunia inflata: the relationship between a self-incompatibility locus F-box protein and its non-self S-RNases.Plant Cell. 2013 Feb;25(2):470-85. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.106294. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23444333 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of PiSSK1 reveals essential role of S-locus F-box protein-containing SCF complexes in recognition of non-self S-RNases during cross-compatible pollination in self-incompatible Petunia inflata.Plant Reprod. 2018 Jun;31(2):129-143. doi: 10.1007/s00497-017-0314-1. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Plant Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29192328
-
The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 physically interacts with S-RNases that may be inhibited by the ubiquitin/26S proteasome pathway of protein degradation during compatible pollination in Antirrhinum.Plant Cell. 2004 Mar;16(3):582-95. doi: 10.1105/tpc.017673. Epub 2004 Feb 18. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 14973168 Free PMC article.
-
Self-incompatibility in Petunia: a self/nonself-recognition mechanism employing S-locus F-box proteins and S-RNase to prevent inbreeding.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012 Mar-Apr;1(2):267-75. doi: 10.1002/wdev.10. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 23801440 Review.
-
S-RNase-based self-incompatibility in Petunia inflata.Ann Bot. 2011 Sep;108(4):637-46. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq253. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Ann Bot. 2011. PMID: 21193481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a Skp1-like protein interacting with SFB, the pollen S determinant of the gametophytic self-incompatibility in Prunus.Plant Physiol. 2012 Jul;159(3):1252-62. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.197343. Epub 2012 May 1. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22548785 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Petunia inflata S-Locus F-box protein (Pi SLF) with Pi SLF like proteins reveals its unique function in S-RNase based self-incompatibility.Plant Cell. 2007 Nov;19(11):3593-609. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055426. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 18024566 Free PMC article.
-
Plant biology research comes of age in China.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):2855-64. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.045393. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17170389 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Self-compatibility in 'Zaohong' Japanese apricot is associated with the loss of function of pollen S genes.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Nov;40(11):6485-93. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2765-2. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24062077 Free PMC article.
-
S locus-linked F-box genes expressed in anthers of Hordeum bulbosum.Plant Cell Rep. 2009 Sep;28(9):1453-60. doi: 10.1007/s00299-009-0745-8. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Plant Cell Rep. 2009. PMID: 19636562
References
-
- Crane, M.B., and Lewis, D. (1942). Genetical studies in pears. III. Incompatibility and sterility. J. Genet. 43, 31–42.
-
- Cronquist, A. (1981). An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants. (New York: Columbia University Press).
-
- Despres, C., Saba-el-Leil, M., Rivard, S., Morse, D., and Cappadocia, M. (1994). Molecular cloning of two Solanum chacoense S-alleles and a hypothesis concerning their evolution. Sex. Plant Reprod. 7, 169–176.
-
- de Nettancourt, D. (2001). Incompatibility and Incongruity in Wild and Cultivated Plants. (Berlin: Springer-Verlag).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

