Reversal of parkinsonism and portosystemic encephalopathy following embolization of a congenital intrahepatic venous shunt: brain MR imaging and 1H spectroscopic findings
- PMID: 15313718
- PMCID: PMC7976519
Reversal of parkinsonism and portosystemic encephalopathy following embolization of a congenital intrahepatic venous shunt: brain MR imaging and 1H spectroscopic findings
Abstract
Parkinsonism and portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) are cerebral disorders associated with motor and neuropsychological dysfunctions that may occur in patients with chronic liver disease. We describe a patient with parkinsonism and neuroradiologic and 1H spectroscopic findings of PSE associated with a large congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt. Chronic liver disease was absent. After endovascular treatment, we documented a progressive reversal of parkinsonism and PSE on the basis of clinical, neuroradiologic, and spectroscopic criteria.
Figures
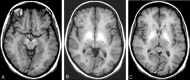
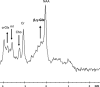
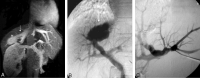
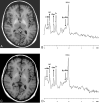
Similar articles
-
Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1998 Sep-Oct;21(5):421-4. doi: 10.1007/s002709900291. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9853150 Review.
-
Hepatic encephalopathy secondary to intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt: balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous embolization with n-butyl cyanoacrylate and microcoils.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2002 May-Jun;25(3):219-21. doi: 10.1007/s00270-001-0110-y. Epub 2002 Mar 27. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2002. PMID: 12058220
-
Multiple intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts: treatment by portal vein embolization.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1993 Jan-Feb;16(1):49-51. doi: 10.1007/BF02603038. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1993. PMID: 8435837
-
Symptomatic intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt: embolization with an alternative approach.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003 Jul;181(1):71-8. doi: 10.2214/ajr.181.1.1810071. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. PMID: 12818832
-
[Congenital intrahepatic venous shunt as a cause of hepatic encephalopathy].Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995 Nov;18(9):460-3. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995. PMID: 8521222 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Manganese accumulation in the brain: MR imaging.Neuroradiology. 2007 Sep;49(9):715-20. doi: 10.1007/s00234-007-0243-z. Epub 2007 Jul 12. Neuroradiology. 2007. PMID: 17624522 Review.
-
Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children.Children (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;9(2):243. doi: 10.3390/children9020243. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shunt occlusion for portosystemic shunt syndrome related refractory hepatic encephalopathy-A single-center experience in 21 patients from Kerala.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep;36(5):411-419. doi: 10.1007/s12664-017-0787-8. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29124669
-
Cirrhosis presenting as Parkinsonism.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2008 Jul;11(3):179-81. doi: 10.4103/0972-2327.42938. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2008. PMID: 19893665 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital portosystemic venous shunt.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 Mar;177(3):285-294. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-3058-x. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29243189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Butterworth RF. Complications of cirrhosis III: hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2000;32(suppl 1):S171–S180 - PubMed
-
- Krieger S, Jauss M, Jansen O, et al. MRI findings in chronic hepatic encephalopathy depend on portosystemic shunt: results of a controlled prospective clinical investigation. J Hepatol 1997;27:121–126 - PubMed
-
- Raskin NH, Price JB, Fishman RA. Portosystemic encephalopathy due to congenital intrahepatic shunts. N Engl J Med 1964;270:225–229 - PubMed
-
- Akahoshi T, Nishizaki T, Wakasugi K, et al. Portal-systemic encephalopathy due to a congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt: three cases and literature review. Hepato-Gastroenterology 2000;47:1113–1116 - PubMed
-
- Inoue E, Hori S, Narumi Y, et al. Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MR images. Radiology 1991;179:551–555 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
