Radixin deficiency causes deafness associated with progressive degeneration of cochlear stereocilia
- PMID: 15314067
- PMCID: PMC2172208
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200402007
Radixin deficiency causes deafness associated with progressive degeneration of cochlear stereocilia
Abstract
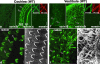
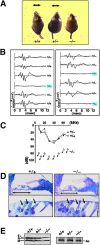
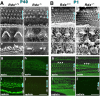
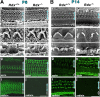
Ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins cross-link actin filaments to plasma membranes to integrate the function of cortical layers, especially microvilli. We found that in cochlear and vestibular sensory hair cells of adult wild-type mice, radixin was specifically enriched in stereocilia, specially developed giant microvilli, and that radixin-deficient (Rdx(-)(/)(-)) adult mice exhibited deafness but no obvious vestibular dysfunction. Before the age of hearing onset ( approximately 2 wk), in the cochlea and vestibule of Rdx(-)(/)(-) mice, stereocilia developed normally in which ezrin was concentrated. As these Rdx(-)(/)(-) mice grew, ezrin-based cochlear stereocilia progressively degenerated, causing deafness, whereas ezrin-based vestibular stereocilia were maintained normally in adult Rdx(-)(/)(-) mice. Thus, we concluded that radixin is indispensable for the hearing ability in mice through the maintenance of cochlear stereocilia, once developed. In Rdx(-)(/)(-) mice, ezrin appeared to compensate for radixin deficiency in terms of the development of cochlear stereocilia and the development/maintenance of vestibular stereocilia. These findings indicated the existence of complicate functional redundancy in situ among ERM proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CLIC5 stabilizes membrane-actin filament linkages at the base of hair cell stereocilia in a molecular complex with radixin, taperin, and myosin VI.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2014 Jan;71(1):61-78. doi: 10.1002/cm.21159. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 24285636 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations of the RDX gene cause nonsyndromic hearing loss at the DFNB24 locus.Hum Mutat. 2007 May;28(5):417-23. doi: 10.1002/humu.20469. Hum Mutat. 2007. PMID: 17226784
-
Mutations of the mouse ELMO domain containing 1 gene (Elmod1) link small GTPase signaling to actin cytoskeleton dynamics in hair cell stereocilia.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036074. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558334 Free PMC article.
-
[ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) as crosslinkers between actin filaments and plasma membranes].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996 Sep;41(12 Suppl):1899-905. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996. PMID: 8890653 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) family: from cytoskeleton to signal transduction.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997 Feb;9(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(97)80154-8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9013673 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular sphingosine kinase 2-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates epidermal growth factor-induced ezrin-radixin-moesin phosphorylation and cancer cell invasion.FASEB J. 2015 Nov;29(11):4654-69. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-274340. Epub 2015 Jul 24. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 26209696 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ entry through mechanotransduction channels localizes BAIAP2L2 to stereocilia tips.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Apr 1;33(4):br6. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-10-0491. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35044843 Free PMC article.
-
Human hereditary hearing impairment: mouse models can help to solve the puzzle.Hum Genet. 2008 Nov;124(4):325-48. doi: 10.1007/s00439-008-0556-y. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18784944 Review.
-
Dynamic length regulation of sensory stereocilia.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008 Dec;19(6):502-10. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.07.006. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18692583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A short splice form of Xin-actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) lacking the Xin repeats is required for maintenance of stereocilia morphology and hearing function.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 4;35(5):1999-2014. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3449-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alagramam, K.N., C.L. Murcia, H.Y. Kwon, K.S. Pawlowski, C.G. Wright, and R.P. Woychik. 2001. The mouse Ames waltzer hearing-loss mutant is caused by mutation of Pcdh15, a novel protocadherin gene. Nat. Genet. 27:99–102. - PubMed
-
- Avraham, K.B., T. Hasson, K.P. Steel, D.M. Kingsley, L.B. Russell, M.S. Mooseker, N.G. Copeland, and N.A. Jenkins. 1995. The mouse Snell's waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nat. Genet. 11:369–375. - PubMed
-
- Belyantseva, I.A., V. Labay, E.T. Boger, A.J. Griffith, and T.B. Friedman. 2003. Stereocilia: the long and the short of it. Trends Mol. Med. 9:458–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

