Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite
- PMID: 15314076
- PMCID: PMC2211939
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040590
Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite
Abstract
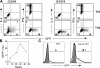
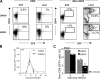
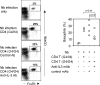
Using mice in which the eGfp gene replaced the first exon of the Il4 gene (G4 mice), we examined production of interleukin (IL)-4 during infection by the intestinal nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nb). Nb infection induced green fluorescent protein (GFP)pos cells that were FcepsilonRIpos, CD49bbright, c-kitneg, and Gr1neg. These cells had lobulated nuclei and granules characteristic of basophils. They were found mainly in the liver and lung, to a lesser degree in the spleen, but not in the lymph nodes. Although some liver basophils from naive mice express GFP, Nb infection enhanced GFP expression and increased the number of tissue basophils. Similar basophil GFP expression was found in infected Stat6-/- mice. Basophils did not increase in number in infected Rag2-/- mice; Rag2-/- mice reconstituted with CD4 T cells allowed significant basophil accumulation, indicating that CD4 T cells can direct both tissue migration of basophils and enhanced IL-4 production. IL-4 production was immunoglobulin independent and only partially dependent on IL-3. Thus, infection with a parasite that induces a "Th2-type response" resulted in accumulation of tissue basophils, and these cells, stimulated by a non-FcR cross-linking mechanism, are a principal source of in vivo IL-4 production.
Figures




References
-
- Seder, R.A., and W.E. Paul. 1994. Acquisition of lymphokine-producing phenotype by CD4+ T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12:635–673. - PubMed
-
- Finkelman, F.D., J. Holmes, I.M. Katona, J.F. Urban Jr., M.P. Beckmann, L.S. Park, K.A. Schooley, R.L. Coffman, T.R. Mosmann, and W.E. Paul. 1990. Lymphokine control of in vivo immunoglobulin isotype selection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8:303–333. - PubMed
-
- Finkelman, F.D., T. Shea-Donohue, J. Goldhill, C.A. Sullivan, S.C. Morris, K.B. Madden, W.C. Gause, and J.F. Urban Jr. 1997. Cytokine regulation of host defense against parasitic gastrointestinal nematodes: lessens from studies with rodent models. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:505–533. - PubMed
-
- Naramura, M., R.J. Hu, and H. Gu. 1998. Mice with a fluorescent marker for interleukin 2 gene activation. Immunity. 9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Hu-li, J., C. Pannetier, L. Guo, M. Lohning, H. Gu, C. Watson, M. Assenmacher, A. Radbruch, and W.E. Paul. 2001. Regulation of expression of IL-4 alleles: analysis using a chimeric GFP/IL-4 gene. Immunity. 14:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

