Hyperresponse to T-cell receptor signaling and apoptosis of Id1 transgenic thymocytes
- PMID: 15314144
- PMCID: PMC506975
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7313-7323.2004
Hyperresponse to T-cell receptor signaling and apoptosis of Id1 transgenic thymocytes
Abstract
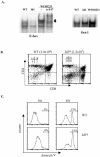
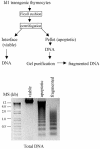
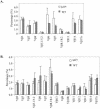
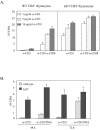
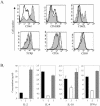
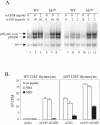
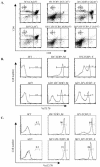
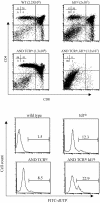
The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors, E2A and HEB, play important roles in T-cell development at multiple checkpoints. Expression of their inhibitor, Id1, abolishes the function of both transcription factors in a dose-dependent manner. The Id1 transgenic thymus is characterized by an accumulation of CD4- CD8- CD44+ CD25- thymocytes, a dramatic reduction of CD4+ CD8+ thymocytes, and an abundance of apoptotic cells. Here we show that these apoptotic cells carry functional T-cell receptors (TCRs), suggesting that apoptosis occurs during T-cell maturation. In contrast, viable Id1 transgenic CD4 single positive T cells exhibit costimulation-independent proliferation upon treatment with anti-CD3 antibody, probably due to a hyperresponse to TCR signaling. Furthermore, Id1 expression causes apoptosis of CD4 and CD8 double- or single-positive thymocytes in HY- or AND-TCR transgenic mice under conditions that normally support positive selection. Collectively, these results suggest that E2A and HEB proteins are crucial for controlling the threshold for TCR signaling, and Id1 expression lowers the threshold, resulting in apoptosis of developing thymocytes.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures
Similar articles
-
Massive apoptosis of thymocytes in T-cell-deficient Id1 transgenic mice.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):8240-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.8240. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567549 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role for HEB downstream or parallel to the pre-TCR signaling pathway during alpha beta thymopoiesis.J Immunol. 1999 Sep 15;163(6):3331-43. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10477603
-
Id1 potentiates NF-kappaB activation upon T cell receptor signaling.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 17;281(46):34989-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608078200. Epub 2006 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17012234
-
The function of E- and Id proteins in lymphocyte development.Nat Rev Immunol. 2001 Dec;1(3):193-9. doi: 10.1038/35105060. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11905828 Review.
-
[The roles of orphan nuclear receptors in T-lymphocyte development in the thymus].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009 Oct 29;63:522-36. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009. PMID: 19940330 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Id1 attenuates Notch signaling and impairs T-cell commitment by elevating Deltex1 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;29(17):4640-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00119-09. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19564409 Free PMC article.
-
Id1 and PD-1 Combined Blockade Impairs Tumor Growth and Survival of KRAS-mutant Lung Cancer by Stimulating PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 28;12(11):3169. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113169. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33126649 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Notch activation is advantageous but not essential for T cell lymphomagenesis in Id1 transgenic mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032944. Epub 2012 Feb 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22393458 Free PMC article.
-
The divergence between T cell and innate lymphoid cell fates controlled by E and Id proteins.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 10;13:960444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960444. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput RNAi screen for detection of immune-checkpoint molecules that mediate tumor resistance to cytotoxic T lymphocytes.EMBO Mol Med. 2015 Apr;7(4):450-63. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404414. EMBO Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25691366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acuto, O., and F. Michel. 2003. CD28-mediated co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:939-951. - PubMed
-
- Bain, G., C. B. Cravatt, C. Loomans, J. Alberola-Ila, S. M. Hedrick, and C. Murre. 2001. Regulation of the helix-loop-helix proteins, E2A and Id3, by the Ras- ERK MAPK cascade. Nat. Immunol. 2:165-171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
