Disruption of the SH2-B gene causes age-dependent insulin resistance and glucose intolerance
- PMID: 15314154
- PMCID: PMC506995
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7435-7443.2004
Disruption of the SH2-B gene causes age-dependent insulin resistance and glucose intolerance
Abstract
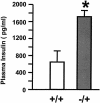
Insulin regulates glucose homeostasis by binding and activating the insulin receptor, and defects in insulin responses (insulin resistance) induce type 2 diabetes. SH2-B, an Src homology 2 (SH2) and pleckstrin homology domain-containing adaptor protein, binds via its SH2 domain to insulin receptor in response to insulin; however, its physiological role remains unclear. Here we show that SH2-B was expressed in the liver, skeletal muscle, and fat. Systemic deletion of SH2-B impaired insulin receptor activation and signaling in the liver, skeletal muscle, and fat, including tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) and IRS2 and activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and the Erk1/2 pathways. Consequently, SH2-B-/- knockout mice developed age-dependent hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and glucose intolerance. Moreover, SH2-B directly enhanced autophosphorylation of insulin receptor and tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS2 in an SH2 domain-dependent manner in cultured cells. Our data suggest that SH2-B is a physiological enhancer of insulin receptor activation and is required for maintaining normal insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis during aging.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adapter protein with a pleckstrin homology (PH) and an Src homology 2 (SH2) domain (APS) and SH2-B enhance insulin-receptor autophosphorylation, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signalling.Biochem J. 2003 Apr 15;371(Pt 2):405-12. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021589. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12521378 Free PMC article.
-
SH2-B promotes insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1)- and IRS2-mediated activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in response to leptin.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 15;279(42):43684-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408495200. Epub 2004 Aug 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15316008 Free PMC article.
-
GTK tyrosine kinase-induced alteration of IRS-protein signalling in insulin producing cells.Mol Med. 2002 Nov;8(11):705-13. Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12520087 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin signalling.J Cell Sci. 2001 Apr;114(Pt 8):1429-30. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.8.1429. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11282018 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nutritionally induced insulin resistance and receptor defect leading to beta-cell failure in animal models.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Nov 18;892:223-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07798.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10842665 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatic TRAF2 regulates glucose metabolism through enhancing glucagon responses.Diabetes. 2012 Mar;61(3):566-73. doi: 10.2337/db11-0474. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22315325 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal SH2B1 is essential for controlling energy and glucose homeostasis.J Clin Invest. 2007 Feb;117(2):397-406. doi: 10.1172/JCI29417. Epub 2007 Jan 18. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17235396 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin receptor-expressing neuron Sh2b1 supports sympathetic nervous system and protects against obesity and metabolic disease.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 23;11(1):1517. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15328-3. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32251290 Free PMC article.
-
SH2B1 Defends Against Energy Imbalance, Obesity, and Metabolic Disease via a Paraventricular Hypothalamus→Dorsal Raphe Nucleus Neurocircuit.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(31):e2400437. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400437. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38885417 Free PMC article.
-
SH2B1 enhances insulin sensitivity by both stimulating the insulin receptor and inhibiting tyrosine dephosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins.Diabetes. 2009 Sep;58(9):2039-47. doi: 10.2337/db08-1388. Epub 2009 Jun 19. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19542202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre, V., T. Uchida, L. Yenush, R. Davis, and M. F. White. 2000. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 275:9047-9054. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre, V., E. D. Werner, J. Giraud, Y. H. Lee, S. E. Shoelson, and M. F. White. 2002. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 277:1531-1537. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, Z., and T. S. Pillay. 2003. Adapter protein with a pleckstrin homology (PH) and an Src homology 2 (SH2) domain (APS) and SH2-B enhance insulin-receptor autophosphorylation, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signalling. Biochem. J. 371:405-412. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed, Z., B. J. Smith, and T. S. Pillay. 2000. The APS adapter protein couples the insulin receptor to the phosphorylation of c-Cbl and facilitates ligand-stimulated ubiquitination of the insulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 475:31-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
