MUC20 suppresses the hepatocyte growth factor-induced Grb2-Ras pathway by binding to a multifunctional docking site of met
- PMID: 15314156
- PMCID: PMC506992
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7456-7468.2004
MUC20 suppresses the hepatocyte growth factor-induced Grb2-Ras pathway by binding to a multifunctional docking site of met
Abstract
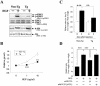
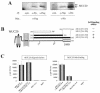
A cDNA encoding a novel mucin protein, MUC20, was isolated as a gene that is up-regulated in the renal tissues of patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. We demonstrate here that the C terminus of MUC20 associates with the multifunctional docking site of Met without ligand activation, preventing Grb2 recruitment to Met and thus attenuating hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced transient extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1 and -2 activation. Production of MUC20 reduced HGF-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression and proliferation, which require the Grb2-Ras pathway, whereas cell scattering, branching morphogenesis, and survival via the Gab1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways was not affected. Thus, MUC20 reduces HGF-induced activation of the Grb2-Ras pathway but not the Gab1/PI3K pathways. We further demonstrate that the cytoplasmic domain of MUC20 has the ability to oligomerize and that the oligomerization augments its affinity for Met. Taken together, these results suggest that MUC20 is a novel regulator of the Met signaling cascade which has a role in suppression of the Grb2-Ras pathway.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures





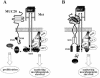
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene by the oncogene Tpr-Met involves GRB2.Oncogene. 1997 Feb 13;14(6):705-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200879. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9038378
-
Concomitant activation of pathways downstream of Grb2 and PI 3-kinase is required for MET-mediated metastasis.Oncogene. 1999 Feb 4;18(5):1139-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202607. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10022119
-
Gab1 coupling to the HGF/Met receptor multifunctional docking site requires binding of Grb2 and correlates with the transforming potential.Oncogene. 1997 Dec 18;15(25):3103-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201561. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9444958
-
HGF/SF-met signaling in the control of branching morphogenesis and invasion.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Feb 1;88(2):408-17. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10358. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12520544 Review.
-
Met receptor tyrosine kinase: enhanced signaling through adapter proteins.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 20;19(49):5582-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203859. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114738 Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing of MUC20 suppresses the malignant character of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells through inhibition of the HGF/MET pathway.Oncogene. 2018 Nov;37(46):6041-6053. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0403-0. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29993037 Free PMC article.
-
Two Cases of Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis With Contrasting Clinical Phenotypes: Genetic Insights.Cureus. 2024 Mar 12;16(3):e56023. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56023. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38606235 Free PMC article.
-
Gene signature for prognosis in comparison of pancreatic cancer patients with diabetes and non-diabetes.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 11;8:e10297. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10297. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240632 Free PMC article.
-
Mucin 20 modulates proteasome capacity through c-Met signalling to increase carfilzomib sensitivity in mantle cell lymphoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Nov;25(21):10164-10174. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16953. Epub 2021 Oct 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34651428 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling ER dimerization dynamics in endocrine disruption based on a BRET-focused approach.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025 Apr 28;29(1):282-295. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2025.2481984. eCollection 2025. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 40304013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boccaccio, C., M. Ando', and P. M. Comoglio. 2002. A differentiation switch for genetically modified hepatocytes. FASEB J. 16:120-122. - PubMed
-
- Comoglio, P. M., and C. Boccaccio. 1996. The HGF receptor family: unconventional signal transducers for invasive cell growth. Genes Cells 1:347-354. - PubMed
-
- Di Renzo, M. F., R. P. Narsimhan, M. Olivero, S. Bretti, S. Giordano, E. Medico, P. Gaglia, P. Zara, and P. M. Comoglio. 1991. Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene 6:1997-2003. - PubMed
-
- Gandino, L., P. Longati, E. Medico, M. Prat, and P. M. Comoglio. 1994. Phosphorylation of serine 985 negatively regulates the hepatocyte growth factor receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 269:1815-1820. - PubMed
-
- Grisendi, S., B. Chambraud, I. Gout, P. M. Comoglio, and T. Crepaldi. 2001. Ligand-regulated binding of FAP68 to the hepatocyte growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276:46632-46638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
