The N-terminal regulatory domain of Stp1p is modular and, fused to an artificial transcription factor, confers full Ssy1p-Ptr3p-Ssy5p sensor control
- PMID: 15314160
- PMCID: PMC506990
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7503-7513.2004
The N-terminal regulatory domain of Stp1p is modular and, fused to an artificial transcription factor, confers full Ssy1p-Ptr3p-Ssy5p sensor control
Abstract
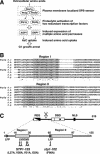
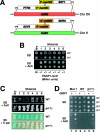
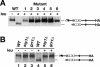
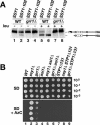
Stp1p and Stp2p are homologous and redundant transcription factors that are synthesized as latent cytoplasmic proteins with N-terminal regulatory domains. In response to extracellular amino acids, the plasma membrane-localized Ssy1p-Ptr3p-Ssy5p (SPS) sensor induces an endoproteolytic processing event that cleaves away the N-terminal regulatory domains. The shorter forms of Stp1p and Stp2p are targeted to the nucleus, where they bind and activate the transcription of amino acid permease genes. A novel genetic screen, specifically designed to search for rare mutations that affect the SPS-sensing pathway, identified the F-box protein Grr1p as an obligatory factor required for Stp1p/Stp2p processing. Additionally, we have found that a null mutation in the ASI1 (amino acid sensor-independent) gene enables full-length unprocessed Stp1p/Stp2p to enter the nucleus and derepress SPS sensor-dependent genes. The N-terminal domains of Stp1p/Stp2p contain two conserved motifs that are required for proper nuclear exclusion and proteolytic processing. These motifs function in parallel; mutations that abolish processing inhibit signaling, whereas mutations that interfere with cytoplasmic retention result in constitutive derepression of SPS sensor-regulated genes independently of processing. The N-terminal domain of Stp1p is functionally autonomous and transferable to other transcription factors, where its presence confers ASI1-dependent nuclear exclusion and SPS sensor-induced proteolytic processing.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures



References
-
- Andréasson, C., E. P. A. Neve, and P. O. Ljungdahl. 2004. Four permeases import proline and the toxic proline analogue azetidine-2-carboxylate into yeast. Yeast 21:193-199. - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc, P., and T. B. Kornberg. 1999. Ci: a complex transducer of the hedgehog signal. Trends Genet. 15:458-462. - PubMed
-
- Baron, M. 2003. An overview of the Notch signalling pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 14:113-119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
