Triplex DNA-mediated downregulation of Ets2 expression results in growth inhibition and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 15314206
- PMCID: PMC514370
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh744
Triplex DNA-mediated downregulation of Ets2 expression results in growth inhibition and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
Abstract
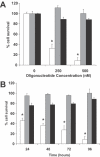
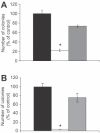
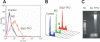
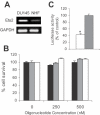
Ets2 is a member of the Ets family of transcription factors that in humans comprise 25 distinct members. Various Ets-domain transcription factors have been implicated in cancer development. Ets2 is expressed in prostate and breast cancer cells and is thought to have a role in promoting growth and survival in these cell types. However, a definitive role and the mechanisms whereby Ets2 acts in cancer cells are still unclear. Structural and functional similarities as well as overlapping DNA binding specificities complicate the identification of the specific roles of the various Ets factors. In this study, we used a triplex-forming oligonucleotide (TFO) to selectively inhibit Ets2 transcription in prostate cancer cells. We had previously shown that the Ets2-targeting TFO, which was directed to a unique purine-rich sequence critical for Ets2 promoter activity, acted with a high degree of sequence-specificity and target selectivity. TFO-mediated downregulation of Ets2 in prostate cancer cells induced important phenotypic changes, including inhibition of anchorage-dependent and anchorage -independent growth, cell cycle alterations and induction of apoptotic cell death. Expression of Ets2 under the control of a heterologous promoter abolished the anti-proliferative effects of the TFO in both short- and long-term assays, suggesting that these effects were a direct result of downregulation of Ets2 transcription and confirming target selectivity of the TFO. Furthermore, normal human fibroblasts, which expressed low levels of Ets2, were not affected by the Ets2-targeting TFO. Downregulation of Ets2 in prostate cancer cells was associated with reduced levels of the anti-apoptotic protein bcl-x(L) and growth regulatory factors cyclin D1 and c-myc. These data revealed a specific role of this transcription factor in promoting growth and survival of prostate cancer cells. Furthermore, the activity and selectivity of the Ets2-targeting TFO suggest that it might represent a valid approach to prostate cancer therapy.
Figures




References
-
- Gewirtz A.M., Sokol,D.L. and Ratajczak,M.Z. (1998) Nucleic acid therapeutics: state of the art and future prospects. Blood, 92, 712–736. - PubMed
-
- Dorsett Y. and Tuschl,T. (2004) siRNAs: applications in functional genomics and potential as therapeutics. Nature Rev. Drug Discov., 3, 318–329. - PubMed
-
- Chan P.P. and Glazer,P.M. (1997) Triplex DNA: fundamentals, advances, and potential applications for gene therapy. J. Mol. Med., 75, 267–282. - PubMed
-
- Praseuth D., Guieysse,A.L. and Helene,C. (1999) Triple helix formation and the antigene strategy for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 181–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

