The telomeric protein TRF2 binds the ATM kinase and can inhibit the ATM-dependent DNA damage response
- PMID: 15314656
- PMCID: PMC509302
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020240
The telomeric protein TRF2 binds the ATM kinase and can inhibit the ATM-dependent DNA damage response
Abstract
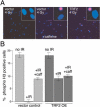
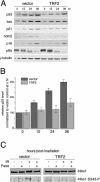
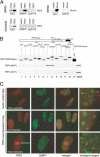
The telomeric protein TRF2 is required to prevent mammalian telomeres from activating DNA damage checkpoints. Here we show that overexpression of TRF2 affects the response of the ATM kinase to DNA damage. Overexpression of TRF2 abrogated the cell cycle arrest after ionizing radiation and diminished several other readouts of the DNA damage response, including phosphorylation of Nbs1, induction of p53, and upregulation of p53 targets. TRF2 inhibited autophosphorylation of ATM on S1981, an early step in the activation of this kinase. A region of ATM containing S1981 was found to directly interact with TRF2 in vitro, and ATM immunoprecipitates contained TRF2. We propose that TRF2 has the ability to inhibit ATM activation at telomeres. Because TRF2 is abundant at chromosome ends but not elsewhere in the nucleus, this mechanism of checkpoint control could specifically block a DNA damage response at telomeres without affecting the surveillance of chromosome internal damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

References
-
- Alligood KJ, Milla M, Rhodes N, Ellis B, Kilpatrick KE, et al. Monoclonal antibodies generated against recombinant ATM support kinase activity. Hybridoma. 2000;19:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, Cech TR. Pot1, the putative telomere end-binding protein in fission yeast and humans. Science. 2001;292:1171–1175. - PubMed
-
- Broccoli D, Smogorzewska A, Chong L, de Lange T. Human telomeres contain two distinct Myb-related proteins, TRF1 and TRF2. Nat Genet. 1997;17:231–235. - PubMed
-
- Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, et al. Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science. 1998;281:1677–1679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 GM059413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM07739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049046/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM59413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG016642/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM56888/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM049046/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056888/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA71387/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM49046/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA21765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG016642/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA071387/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016642/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

