Membrane position of a basic aromatic peptide that sequesters phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate determined by site-directed spin labeling and high-resolution NMR
- PMID: 15315949
- PMCID: PMC1304792
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.046748
Membrane position of a basic aromatic peptide that sequesters phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate determined by site-directed spin labeling and high-resolution NMR
Abstract
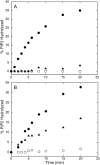
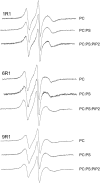
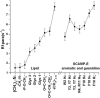
The membrane interactions and position of a positively charged and highly aromatic peptide derived from a secretory carrier membrane protein (SCAMP) are examined using magnetic resonance spectroscopy and several biochemical methods. This peptide (SCAMP-E) is shown to bind to membranes containing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PI(4,5)P2, and sequester PI(4,5)P2 within the plane of the membrane. Site-directed spin labeling of the SCAMP-E peptide indicates that the position and structure of membrane bound SCAMP-E are not altered by the presence of PI(4,5)P2, and that the peptide backbone is positioned within the lipid interface below the level of the lipid phosphates. A second approach using high-resolution NMR was used to generate a model for SCAMP-E bound to bicelles. This approach combined oxygen enhancements of nuclear relaxation with a computational method to dock the SCAMP-E peptide at the lipid interface. The model for SCAMP generated by NMR is consistent with the results of site-directed spin labeling and places the peptide backbone in the bilayer interfacial region and the aromatic side chains within the lipid hydrocarbon region. The charged side chains of SCAMP-E lie well within the interface with two arginine residues lying deeper than a plane defined by the position of the lipid phosphates. These data suggest that SCAMP-E interacts with PI(4,5)P2 through an electrostatic mechanism that does not involve specific lipid-peptide contacts. This interaction may be facilitated by the position of the positively charged side chains on SCAMP-E within a low-dielectric region of the bilayer interface.
Figures




References
-
- Altenbach, C., K. J. Oh, R. J. Trabanino, K. Hideg, and W. L. Hubbell. 2001. Estimation of inter-residue distances in spin labeled proteins at physiological temperatures: experimental strategies and practical limitations. Biochemistry. 40:15471–15482. - PubMed
-
- Arbuzova, A., L. Wang, J. Wang, G. Hangyas-Mihalyne, D. Murray, B. Honig, and S. McLaughlin. 2000. Membrane binding of peptides containing both basic and aromatic residues. Experimental studies with peptides corresponding to the scaffolding region of caveolin and the effector region of MARCKS. Biochemistry. 39:10330–10339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

