Transcription factor YY1 associates with pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA in cycling but not in quiescent (G0) cells
- PMID: 15316102
- PMCID: PMC514366
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh737
Transcription factor YY1 associates with pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA in cycling but not in quiescent (G0) cells
Abstract
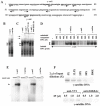
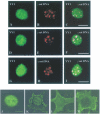
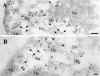
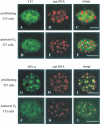
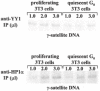
Pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA is organized in constitutive heterochromatin structures. It comprises a 234 bp sequence repeated several thousands times surrounding the centromeric sequence of all murine chromosomes. Potential binding sites for transcription factor Yin Yang 1 (YY1), a repressor or activator of several cellular and viral genes, are present in pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA. Using gel retardation and chromatin immunoprecipitation, we demonstrate in this work that YY1 specifically interacts in vitro and in vivo with gamma-satellite DNA. Using immunoFISH and confocal microscopy we show that YY1 specifically co-localizes with pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA clusters organized in constitutive heterochromatin in murine L929 and 3T3 fibroblasts cell lines. Immunoelectron microscopy experiments further confirmed YY1 localization in heterochromatic areas. Overall, our results demonstrate for the first time that a fraction of YY1 is directly associated with constitutive heterochromatin structures. This association appears physiologically relevant since the association of YY1 with pericentromeric gamma-satellite DNA observed in cycling 3T3 fibroblasts strongly diminished in quiescent (G0) 3T3 fibroblasts. We discuss the implications of these results in the context of heterochromatin formation as well as with regard to the YY1-induced repression of euchromatic genes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Yin Yang-1 (YY1) protein undergoes a DNA-replication-associated switch in localization from the cytoplasm to the nucleus at the onset of S phase.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jan 26;117(Pt 3):465-76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00870. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 14702388
-
Cell cycle-dependent accumulation of histone H3.3 and euchromatic histone modifications in pericentromeric heterochromatin in response to a decrease in DNA methylation levels.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Oct 15;316(17):2731-46. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.06.016. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20599948
-
Epigenetic profiling of heterochromatic satellite DNA.Chromosoma. 2011 Aug;120(4):409-22. doi: 10.1007/s00412-011-0325-x. Epub 2011 May 19. Chromosoma. 2011. PMID: 21594600
-
Pericentromeric satellite RNAs as flexible protein partners in the regulation of nuclear structure.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Jul-Aug;15(4):e1868. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1868. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38973000 Review.
-
Mammalian satellite DNA: a speaking dumb.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2013;90:31-65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-410523-2.00002-X. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23582201 Review.
Cited by
-
Directed targeting of chromatin to the nuclear lamina is mediated by chromatin state and A-type lamins.J Cell Biol. 2015 Jan 5;208(1):33-52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201405110. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25559185 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of YY1 to the proximal region of the murine beta interferon promoter is essential to allow CBP recruitment and K8H4/K14H3 acetylation on the promoter region after virus infection.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(22):8551-61. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00420-06. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16954376 Free PMC article.
-
The POU transcription factor Oct-1 represses virus-induced interferon A gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(19):8717-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.19.8717-8731.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16166650 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferation-dependent and cell cycle regulated transcription of mouse pericentric heterochromatin.J Cell Biol. 2007 Nov 5;179(3):411-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200706176. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17984319 Free PMC article.
-
Functional elements residing within satellite DNAs.EMBO Rep. 2005 Nov;6(11):1035-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400558. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 16264428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomas M.J. and Seto,E. (1999) Unlocking the mechanisms of transcription factor YY1: are chromatin modifying enzymes the key? Gene, 236, 197–208. - PubMed
-
- Austen M., Luscher,B. and Luscher-Firzlaff,J.M. (1997) Characterization of the transcriptional regulator YY1. The bipartite transactivation domain is independent of interaction with the TATA box-binding protein, transcription factor IIB, TAFII55, or cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CBP)-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 1709–1717. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.S., Galvin,K.M., See,R.H., Eckner,R., Livingston,D., Moran,E. and Shi,Y. (1995) Relief of YY1 transcriptional repression by adenovirus E1A is mediated by E1A-associated protein p300. Genes Dev., 9, 1188–1198. - PubMed

