Effects of gemcitabine on APE/ref-1 endonuclease activity in pancreatic cancer cells, and the therapeutic potential of antisense oligonucleotides
- PMID: 15316562
- PMCID: PMC2747714
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602080
Effects of gemcitabine on APE/ref-1 endonuclease activity in pancreatic cancer cells, and the therapeutic potential of antisense oligonucleotides
Abstract
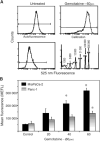
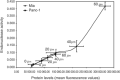
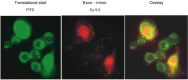
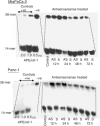
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE) is a key enzyme involved in DNA base excision repair (BER) that is often expressed at elevated levels in human cancers. Pancreatic cancer cells treated with the nucleoside analogue gemcitabine (2', 2'-difluoro-2'deoxycytidine) showed increases in APE/redox effector factor (ref-1) protein levels (approximately two-fold for Panc-1 and six-fold for MiaPaCa-2), with corresponding increases in endonuclease activity. These results suggested that the activation of APE/ref-1 might be an adaptive response that contributes to gemcitabine resistance by facilitating BER. To test this hypothesis, we examined the effects of disrupting APE/ref-1 using antisense on gemcitabine toxicity. Antisense oligonucleotides decreased protein levels three-fold in MiaPaCa-2 and five-fold in Panc-1 in comparison to controls, associated with reduced endonuclease activity. Combination treatments with antisense oligonucleotides and gemcitabine partially suppressed the increase in APE/ref-1 activity seen in cells exposed to gemcitabine alone. While clonogenic assays showed only slight decreases in colony formation in cells treated with either antisense oligonucleotides or gemcitabine alone, the combination with APE/ref-1 antisense resulted in a 2-log enhancement of gemcitabine toxicity in Panc-1 cells. Overall these findings suggest that APE/ref-1 plays a significant role in gemcitabine resistance in some pancreatic cancer cells, and support the further investigation of novel treatments that target this protein.
Figures



References
-
- Abbruzzese JL (2002) Past and present treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: chemotherapy as a standard treatment modality. Semin Oncol 29: 2–8 - PubMed
-
- Arlt A, Gehrz A, Muerkoster S, Vorndamm J, Kruse ML, Folsch UR, Schafer H (2003) Role of NF-kappaB and Akt/PI3K in the resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines against gemcitabine-induced cell death. Oncogene 22: 3243–3251 - PubMed
-
- Arrigo AP (1999) Gene expression and the thiol redox state. Free Radic Biol Med 27: 936–944 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

