Regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 15317799
- PMCID: PMC516831
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.17.5933-5937.2004
Regulation of ribosomal protein synthesis in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
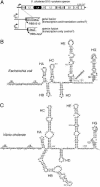
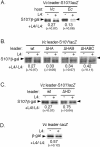
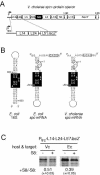
We have investigated the regulation of the S10 and spc ribosomal protein (r-protein) operons in Vibrio cholerae. Both operons are under autogenous control; they are mediated by r-proteins L4 and S8, respectively. Our results suggest that Escherichia coli-like strategies for regulating r-protein synthesis extend beyond the enteric members of the gamma subdivision of proteobacteria.
Figures
References
-
- Cerretti, D. P., L. C. Mattheakis, K. R. Kearney, L. Vu, and M. Nomura. 1988. Translational regulation of the spc operon in Escherichia coli: identification and structural analysis of the target site for S8 repressor protein. J. Mol. Biol. 204:309-329. - PubMed
-
- Gregory, R. R., P. B. F. Cahill, D. L. Thurlow, and R. A. Zimmermann. 1988. Interaction of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 with its binding sites in ribosomal RNA and messenger RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 204:295-307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

