FlhF, the third signal recognition particle-GTPase of Bacillus subtilis, is dispensable for protein secretion
- PMID: 15317803
- PMCID: PMC516824
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.17.5956-5960.2004
FlhF, the third signal recognition particle-GTPase of Bacillus subtilis, is dispensable for protein secretion
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis contains three proteins of the signal recognition particle-GTPase family known as Ffh, FtsY, and FlhF. Here we show that FlhF is dispensable for protein secretion, unlike Ffh and FtsY. Although flhF is located in the fla/che operon, B. subtilis 168 flhF mutant cells assemble flagella and are motile.
Figures

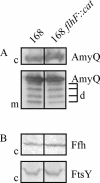

Similar articles
-
Proteomic dissection of potential signal recognition particle dependence in protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis.Proteomics. 2006 Jun;6(12):3636-48. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500560. Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 16705751
-
flhF, a Bacillus subtilis flagellar gene that encodes a putative GTP-binding protein.Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2705-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01447.x. Mol Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1447978
-
The Bacillus subtilis SRP54 homologue, Ffh, has an intrinsic GTPase activity and forms a ribonucleoprotein complex with small cytoplasmic RNA in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 30;199(3):1394-9. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1385. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994. PMID: 7511896
-
[Bacterial signal recognition particles (SRP): comparisons with mammalian SRP on their structure and function].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996 Sep;41(11):1569-79. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 1996. PMID: 8827891 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Bacterial determinants of the social behavior of Bacillus subtilis.Res Microbiol. 2013 Sep;164(7):788-98. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Res Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23791621 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic characterization of FlhF from Bacillus subtilis.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007 May 1;63(Pt 5):449-51. doi: 10.1107/S1744309107020180. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2007. PMID: 17565194 Free PMC article.
-
FlhF(T368A) modulates motility in the bacteriophage carrier state of Campylobacter jejuni.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Nov;110(4):616-633. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14120. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30230632 Free PMC article.
-
Protein transport across and into cell membranes in bacteria and archaea.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jan;67(2):179-99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0160-x. Epub 2009 Oct 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 19823765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The tmRDB and SRPDB resources.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D163-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj142. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381838 Free PMC article.
-
A disulfide bond-containing alkaline phosphatase triggers a BdbC-dependent secretion stress response in Bacillus subtilis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Nov;72(11):6876-85. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01176-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17088376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antelmann, H., H. Tjalsma, B. Voigt, S. Ohlmeier, S. Bron, J. M. van Dijl, and M. Hecker. 2001. A proteomic view on genome-based signal peptide predictions. Genome Res. 11:1484-1502. - PubMed
-
- Blum, H., H. Beier, and H. J. Gross. 1987. Improved silver staining of plant- proteins, RNA and DNA polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93-99.
-
- Bolhuis, A., C. P. Broekhuizen, A. Sorokin, M. L. van Roosmalen, G. Venema, S. Bron, W. J. Quax, J. M. van Dijl. 1998. SecDF of Bacillus subtilis, a molecular Siamese twin required for the efficient secretion of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 273:21217-21224. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter, P. B., D. W. Hanlon, and G. W. Ordal. 1992. flhF, a Bacillus subtilis flagellar gene that encodes a putative GTP-binding protein. Mol. Microbiol. 6:2705-2713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

