Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces hyperexcitable reentrant circuits in the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 15317847
- PMCID: PMC6729760
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2045-04.2004
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces hyperexcitable reentrant circuits in the dentate gyrus
Abstract
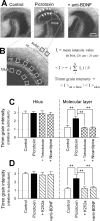
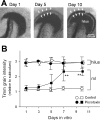
Aberrant sprouting and synaptic reorganization of the mossy fiber (MF) axons are commonly found in the hippocampus of temporal lobe epilepsy patients and result in the formation of excitatory feedback loops in the dentate gyrus, a putative cellular basis for recurrent epileptic seizures. Using ex vivo hippocampal cultures, we show that prolonged hyperactivity induces MF sprouting and the resultant network reorganizations and that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is necessary and sufficient to evoke these pathogenic plasticities. Hyperexcitation induced an upregulation of BDNF protein expression in the MF pathway, an effect mediated by L-type Ca2+ channels. The neurotrophin receptor tyrosine kinase (Trk)B inhibitor K252a or function-blocking anti-BDNF antibody prevented hyperactivity-induced MF sprouting. Even under blockade of neural activity, local application of BDNF to the hilus, but not other subregions, was capable of initiating MF axonal remodeling, eventually leading to dentate hyperexcitability. Transfecting granule cells with dominant-negative TrkB prevented axonal branching. Thus, excessive activation of L-type Ca2+ channels causes granule cells to express BDNF, and extracellularly released BDNF stimulates TrkB receptors present on the hilar segment of the MFs to induce axonal branching, which may establish hyperexcitable dentate circuits.
Figures






References
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP (1995) Hippocampal formation. In: The rat nervous system, Ed 2 (Paxinos C, ed), pp 443-493. New York: Academic.
-
- Ayala GF, Dichter M, Gumnit RJ, Matsumoto H, Spencer WA (1973) Genesis of epileptic interictal spikes. New knowledge of cortical feedback systems suggests a neurophysiological explanation of brief paroxysms. Brain Res 52: 1-17. - PubMed
-
- Babb TL, Kupfer WR, Pretorius JK, Crandall PH, Levesque MF (1991) Synaptic reorganization by mossy fibers in human epileptic fascia dentata. Neuroscience 42: 351-363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
