The role of hippocampal glutamate receptor-A-dependent synaptic plasticity in conditional learning: the importance of spatiotemporal discontiguity
- PMID: 15317854
- PMCID: PMC6729761
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1093-04.2004
The role of hippocampal glutamate receptor-A-dependent synaptic plasticity in conditional learning: the importance of spatiotemporal discontiguity
Abstract
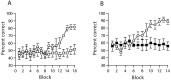
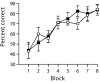
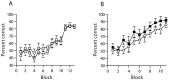
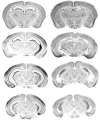
Gene-targeted mice lacking the AMPA receptor subunit glutamate receptor-A (GluR-A or GluR1) and mice with cytotoxic hippocampal lesions were compared with wild-type and sham-operated controls, respectively, on a conditional learning task using an elevated T-maze. Floor inserts (white perspex vs wire mesh) provided a conditional cue indicating in which goal arm a food reward was to be found. The relationship between the floor insert and the rewarded goal arm was constant throughout the experiment. Both lesioned and knock-out mice were able to acquire the task if the floor inserts extended throughout the entire maze, including the start arm and both goal arms. In contrast, both lesioned and knock-out mice were unable to acquire the task if the floor inserts were only present in the start arm of the maze. The absence of the conditional cue (the floor insert) at the time when the place-reward association was experienced thus critically determined whether or not the mice were impaired. We suggest that hippocampal GluR-A-dependent synaptic plasticity contributes to a memory system in rodents for encoding both the spatial and temporal contexts (the where and the when) associated with a particular event.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NMDA receptor subunit NR2A is required for rapidly acquired spatial working memory but not incremental spatial reference memory.J Neurosci. 2008 Apr 2;28(14):3623-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3639-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18385321 Free PMC article.
-
GluR-A-Deficient mice display normal acquisition of a hippocampus-dependent spatial reference memory task but are impaired during spatial reversal.Behav Neurosci. 2003 Aug;117(4):866-70. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.117.4.866. Behav Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12931971
-
Forebrain-specific glutamate receptor B deletion impairs spatial memory but not hippocampal field long-term potentiation.J Neurosci. 2006 Aug 16;26(33):8428-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5410-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16914668 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the GluR-A (GluR1) AMPA receptor subunit in learning and memory.Prog Brain Res. 2008;169:159-78. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)00009-X. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18394473 Review.
-
Plasticity, hippocampal place cells, and cognitive maps.Arch Neurol. 2001 Jun;58(6):874-81. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.6.874. Arch Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11405801 Review.
Cited by
-
Blast waves from detonated military explosive reduce GluR1 and synaptophysin levels in hippocampal slice cultures.Exp Neurol. 2016 Dec;286:107-115. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27720798 Free PMC article.
-
PKMzeta maintains spatial, instrumental, and classically conditioned long-term memories.PLoS Biol. 2008 Dec 23;6(12):2698-706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060318. PLoS Biol. 2008. PMID: 19108606 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct effects of AMPAR subunit depletion on spatial memory.iScience. 2023 Oct 1;26(11):108116. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108116. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37876813 Free PMC article.
-
Ras and Rap signaling in synaptic plasticity and mental disorders.Neuroscientist. 2011 Feb;17(1):54-78. doi: 10.1177/1073858410365562. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Neuroscientist. 2011. PMID: 20431046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissociations within short-term memory in GluA1 AMPA receptor subunit knockout mice.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Oct 10;224(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.05.016. Epub 2011 May 27. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21641937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannerman DM, Good MA, Butcher SP, Ramsay M, Morris RGM (1995) Distinct components of spatial learning revealed by prior training and NMDA receptor blockade. Nature 378: 182-186. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361: 31-39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
