A novel type of silencing factor, Clr2, is necessary for transcriptional silencing at various chromosomal locations in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- PMID: 15317867
- PMCID: PMC516054
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh780
A novel type of silencing factor, Clr2, is necessary for transcriptional silencing at various chromosomal locations in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Abstract
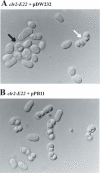
The mating-type region of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe comprises three loci: mat1, mat2-P and mat3-M. mat1 is expressed and determines the mating type of the cell. mat2-P and mat3-M are two storage cassettes located in a 17 kb heterochromatic region with features identical to those of mammalian heterochromatin. Mutations in the swi6+, clr1+, clr2+, clr3+, clr4+ and clr6+ genes were obtained in screens for factors necessary for silencing the mat2-P-mat3-M region. swi6+ encodes a chromodomain protein, clr3+ and clr6+ histone deacetylases, and clr4+ a histone methyltransferase. Here, we describe the cloning and characterization of clr2+. The clr2+ gene encodes a 62 kDa protein with no obvious sequence homologs. Deletion of clr2+ not only affects transcriptional repression in the mating-type region, but also centromeric silencing and silencing of a PolII-transcribed gene inserted in the rDNA repeats. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we show that Clr2 is necessary for histone hypoacetylation in the mating-type region, suggesting that Clr2 acts upstream of histone deacetylases to promote transcriptional silencing.
Figures

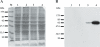

References
-
- Arcangioli B. and Thon,G. (2004) Mating-type cassettes: structure, switching and silencing. In Egel,R. (ed.), The Molecular Biology of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Springer, New York, NY, pp. 129–148.
-
- Egel R., Willer,M. and Nielsen,O. (1989) Unblocking of meiotic crossing-over between the silent mating-type cassettes of fission yeast, conditioned by the pleiotropic mutant rik1. Curr. Genet., 15, 407–410.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

