Selectivity and affinity of triplex-forming oligonucleotides containing 2'-aminoethoxy-5-(3-aminoprop-1-ynyl)uridine for recognizing AT base pairs in duplex DNA
- PMID: 15317869
- PMCID: PMC516051
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh776
Selectivity and affinity of triplex-forming oligonucleotides containing 2'-aminoethoxy-5-(3-aminoprop-1-ynyl)uridine for recognizing AT base pairs in duplex DNA
Abstract
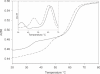
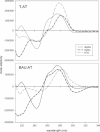
We have used DNase I footprinting, fluorescence and ultraviolet (UV) melting experiments and circular dichroism to demonstrate that, in the parallel triplex binding motif, 2'-aminoethoxy-5-(3-aminoprop-1-ynyl)uridine (bis-amino-U, BAU) has very high affinity for AT relative to all other Watson-Crick base pairs in DNA. Complexes containing two or more substitutions with this nucleotide analogue are stable at pH 7.0, even though they contain several C.GC base triplets. These modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides retain exquisite sequence specificity, with enhanced discrimination against YR base pairs (especially CG). These properties make BAU a useful base analogue for the sequence-specific creation of stable triple helices at pH 7.0.
Figures
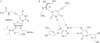




References
-
- Chan P.P. and Glazer,P.M. (1997) Triplex DNA: fundamentals, advances and potential applications for gene therapy. J. Mol. Med., 75, 267–282. - PubMed
-
- Gorman L. and Glazer,P.M. (2001) Directed gene modification by triple helix formation. Curr. Mol. Med., 1, 391–399. - PubMed
-
- Praseuth D., Guieysse,A.L. and Hélène,C. (1999) Triple helix formation and the antigene strategy for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1489, 181–206. - PubMed
-
- Neidle S. (1997) Recent developments in triple-helix regulation of gene expression. Anticancer Drug Des., 12, 433–442. - PubMed
-
- Vasquez K.M. and Wilson,J.H. (1998) Triplex-directed modification of genes and gene activity. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 4–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

