Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome: brain death following hemodialysis for metabolic acidosis and acute renal failure--a case report
- PMID: 15318947
- PMCID: PMC515303
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-5-9
Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome: brain death following hemodialysis for metabolic acidosis and acute renal failure--a case report
Abstract
Background: Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome (DDS) is the clinical phenomenon of acute neurologic symptoms attributed to cerebral edema that occurs during or following intermittent hemodialysis (HD). We describe a case of DDS-induced cerebral edema that resulted in irreversible brain injury and death following acute HD and review the relevant literature of the association of DDS and HD.
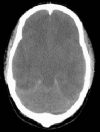
Case presentation: A 22-year-old male with obstructive uropathy presented to hospital with severe sepsis syndrome secondary to pneumonia. Laboratory investigations included a pH of 6.95, PaCO2 10 mmHg, HCO3 2 mmol/L, serum sodium 132 mmol/L, serum osmolality 330 mosmol/kg, and urea 130 mg/dL (46.7 mmol/L). Diagnostic imaging demonstrated multifocal pneumonia, bilateral hydronephrosis and bladder wall thickening. During HD the patient became progressively obtunded. Repeat laboratory investigations showed pH 7.36, HCO3 19 mmol/L, potassium 1.8 mmol/L, and urea 38.4 mg/dL (13.7 mmol/L) (urea-reduction-ratio 71%). Following HD, spontaneous movements were absent with no pupillary or brainstem reflexes. Head CT-scan showed diffuse cerebral edema with effacement of basal cisterns and generalized loss of gray-white differentiation. Brain death was declared.
Conclusions: Death is a rare consequence of DDS in adults following HD. Several features may have predisposed this patient to DDS including: central nervous system adaptations from chronic kidney disease with efficient serum urea removal and correction of serum hyperosmolality; severe cerebral intracellular acidosis; relative hypercapnea; and post-HD hemodynamic instability with compounded cerebral ischemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: A preventable fatal acute complication.Med J Malaysia. 2016 Apr;71(2):91-2. Med J Malaysia. 2016. PMID: 27326954
-
[Acute encephalopathy due to thiamine deficiency with hyperammonemia in a chronic hemodialysis patient: a case report].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2003;45(4):393-7. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2003. PMID: 12806978 Japanese.
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome and other treatment complications of extreme uremia: a rare occurrence yet not vanished.Hemodial Int. 2008 Jul;12(3):301-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2008.00270.x. Hemodial Int. 2008. PMID: 18638082
-
The pathophysiology of the dialysis disequilibrium syndrome.Mayo Clin Proc. 1969 Jun;44(6):406-29. Mayo Clin Proc. 1969. PMID: 4893701 Review. No abstract available.
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: a narrative review.Semin Dial. 2008 Sep-Oct;21(5):493-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-139X.2008.00474.x. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Semin Dial. 2008. PMID: 18764799 Review.
Cited by
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome occurring during continuous renal replacement therapy.Clin Kidney J. 2013 Oct;6(5):526-9. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sft087. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Kidney J. 2013. PMID: 26120445 Free PMC article.
-
Haemodialysis-induced syncope due to Chiari II malformation.NDT Plus. 2011 Dec;4(6):390-1. doi: 10.1093/ndtplus/sfr095. Epub 2011 Aug 2. NDT Plus. 2011. PMID: 25984201 Free PMC article.
-
Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome (DDS) in pediatric patients on dialysis: systematic review and clinical practice recommendations.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Feb;37(2):263-274. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05242-1. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34609583
-
Fatal dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: A tale of two patients.J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2010 Jul;3(3):300. doi: 10.4103/0974-2700.66555. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2010. PMID: 20930984 Free PMC article.
-
Management of hepatic encephalopathy.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014 Jun;16(6):297. doi: 10.1007/s11940-014-0297-2. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24807164
References
-
- Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of acute renal failure: a prospective, multicenter, community-based study. Kidney Internat. 1996;50:811–8181. - PubMed
-
- Arieff A. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome: Current concepts on pathogenesis and prevention. Kidney Internat. 1994;45:629–635. - PubMed
-
- Peterson H. Acute encephalopathy occurring during hemodialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1964;113:877–880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical