Multiplexed genetic analysis using an expanded genetic alphabet
- PMID: 15319316
- PMCID: PMC1592527
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.034330
Multiplexed genetic analysis using an expanded genetic alphabet
Abstract
Background: All states require some kind of testing for newborns, but the policies are far from standardized. In some states, newborn screening may include genetic tests for a wide range of targets, but the costs and complexities of the newer genetic tests inhibit expansion of newborn screening. We describe the development and technical evaluation of a multiplex platform that may foster increased newborn genetic screening.
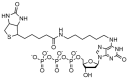
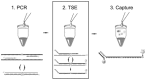
Methods: MultiCode PLx involves three major steps: PCR, target-specific extension, and liquid chip decoding. Each step is performed in the same reaction vessel, and the test is completed in approximately 3 h. For site-specific labeling and room-temperature decoding, we use an additional base pair constructed from isoguanosine and isocytidine. We used the method to test for mutations within the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. The developed test was performed manually and by automated liquid handling. Initially, 225 samples with a range of genotypes were tested retrospectively with the method. A prospective study used samples from >400 newborns.
Results: In the retrospective study, 99.1% of samples were correctly genotyped with no incorrect calls made. In the perspective study, 95% of the samples were correctly genotyped for all targets, and there were no incorrect calls.
Conclusions: The unique genetic multiplexing platform was successfully able to test for 31 targets within the CFTR gene and provides accurate genotype assignments in a clinical setting.
Figures

References
-
- Servais J, Lambert C, Fontaine E, Plesseria JM, Robert I, Arendt V, et al. Comparison of DNA sequencing and a line probe assay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drug resistance mutations in patients failing highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Microbiol 2001;39:454-459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Day NS, Tadin M, Christiano AM, Lanzano P, Piomelli S, Brown S. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell diseases using oligonucleotide ligation assay coupled with laser-induced capillary fluorescence detection. Prenat Diagn 2002;22:686-691. - PubMed
-
- Fulton RJ, McDade RL, Smith PL, Kienker LJ, Kettman JR, Jr. Advanced multiplexed analysis with the FlowMetrix system. Clin Chem 1997;43:1749-1756. - PubMed
-
- Smith PL, WalkerPeach CR, Fulton RJ, DuBois DB. A rapid, sensitive, multiplexed assay for detection of viral nucleic acids using the FlowMetrix system. Clin Chem 1998;44:2054-2056. - PubMed
-
- The San Diego Conference. Nucleic Acid Technology: The Cutting Edge of Discovery. November 6–8, 1997. Abstracts. Clin Chem 1997;43:2213-2224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

