Multiple kinase cascades mediate prolactin signals to activating protein-1 in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 15319452
- PMCID: PMC1634796
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2004-0187
Multiple kinase cascades mediate prolactin signals to activating protein-1 in breast cancer cells
Abstract
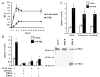
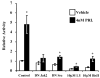
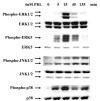
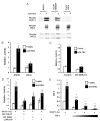
The importance of prolactin (PRL) in physiological proliferation and differentiation of the mammary gland, together with high levels of PRL receptors in breast tumors, the association of circulating PRL with incidence of breast cancer, and the recognition of locally produced PRL, point to the need for greater understanding of PRL actions in mammary disease. Although PRL has been shown to activate multiple kinase cascades in various target cells, relatively little is known of its signaling pathways in the mammary gland apart from the Janus kinase 2/ signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 pathway, particularly in tumor cells. Another potential effector is activating protein-1 (AP-1), a transcription complex that regulates processes essential for neoplastic progression, including proliferation, survival and invasion. We demonstrate that PRL activates AP-1 in MCF-7 cells, detectable at 4 h and sustained for at least 24 h. Although Janus kinase 2 and ERK1/2 are the primary mediators of PRL-induced signals, c-Src, phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase, protein kinase C, and other MAPKs contribute to maximal activity. PRL activation of these pathways leads to increased c-Jun protein and phosphorylation, JunB protein, and phosphorylation of c-Fos, elevating the levels of AP-1 complexes able to bind DNA. These active AP-1 dimers may direct expression of multiple target genes, mediating some of PRL's actions in mammary disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stat5 activation inhibits prolactin-induced AP-1 activity: distinct prolactin-initiated signals in tumorigenesis dependent on cell context.Oncogene. 2007 Sep 20;26(43):6341-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210454. Epub 2007 Apr 16. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17438530 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin and estrogen enhance the activity of activating protein 1 in breast cancer cells: role of extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2-mediated signals to c-fos.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jul;19(7):1765-78. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0339. Epub 2005 Mar 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15746191 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin (PRL)-PRL receptor system increases cell proliferation involving JNK (c-Jun amino terminal kinase) and AP-1 activation: inhibition by glucocorticoids.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Apr;14(4):564-75. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.4.0442. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10770493
-
Role of SRC family kinases in prolactin signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:163-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472538 Review.
-
Progesterone receptors (PR) mediate STAT actions: PR and prolactin receptor signaling crosstalk in breast cancer models.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Feb;176:88-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.04.011. Epub 2017 Apr 23. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28442393 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prolactin-induced mouse mammary carcinomas model estrogen resistant luminal breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Jan 28;13(1):R11. doi: 10.1186/bcr2819. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21276249 Free PMC article.
-
PAK1 regulates breast cancer cell invasion through secretion of matrix metalloproteinases in response to prolactin and three-dimensional collagen IV.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1048-64. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1322. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23744893 Free PMC article.
-
Stiff collagen matrices increase tumorigenic prolactin signaling in breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12722-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.447631. Epub 2013 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23530035 Free PMC article.
-
Stat5 activation inhibits prolactin-induced AP-1 activity: distinct prolactin-initiated signals in tumorigenesis dependent on cell context.Oncogene. 2007 Sep 20;26(43):6341-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210454. Epub 2007 Apr 16. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17438530 Free PMC article.
-
Complex prolactin crosstalk in breast cancer: new therapeutic implications.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009 Aug 13;307(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.03.014. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19524120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vonderhaar BK. Prolactin in human breast cancer development. In: Ethier SP, editor. Endocrine oncology. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2000. pp. 101–120.
-
- Goffin V, Touraine P, Pichard C, Bernichtein S, Kelly PA. Should prolactin be reconsidered as a therapeutic target in human breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999;151:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Michaud S, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Longcope C, Rosner B, Speizer FE. Plasma prolactin levels and subsequent risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999;91:629–634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

