Structural studies of duck delta2 crystallin mutants provide insight into the role of Thr161 and the 280s loop in catalysis
- PMID: 15320872
- PMCID: PMC1134128
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040656
Structural studies of duck delta2 crystallin mutants provide insight into the role of Thr161 and the 280s loop in catalysis
Abstract
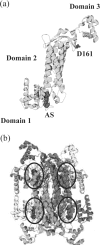
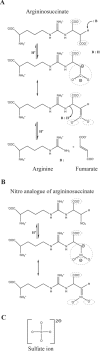
Delta crystallin, a taxon-specific crystallin present in avian eye lenses, is homologous to the urea cycle enzyme ASL (argininosuccinate lyase). Although there are two delta crystallin isoforms in duck lenses, ddeltac1 (duck delta1 crystallin) and ddeltac2 (duck delta2 crystallin), only ddeltac2 is catalytically active. Previous structural studies have suggested that residues Ser283 and His162 in the multi-subunit active site of ddeltac2/ASL are the putative catalytic acid/base, while the highly conserved, positively charged Lys289 is thought to help stabilize the carbanion intermediate. The strict conservation of a small hydroxy-containing residue (Thr or Ser) at position 161 adjacent to the putative catalytic base, as well as its proximity to the substrate in the S283A ddeltac2 enzyme-substrate complex, prompted us to investigate further the role this residue. Structures of the active T161S and inactive T161D ddeltac2 mutants, as well as T161D complexed with argininosuccinate, have been determined to 2.0 A resolution. The structures suggest that a hydroxy group is required at position 161 to help correctly position the side chain of Lys289 and the fumarate moiety of the substrate. Threonine is probably favoured over serine, because the interaction of its methyl group with Leu206 would restrict its conformational flexibility. Residues larger than Thr or Ser interfere with substrate binding, supporting previous suggestions that correct positioning of the substrate's fumarate moiety is essential for catalysis to occur. The presence of the 280s loop (i.e. a loop formed by residues 270-290) in the 'open' conformation suggests that loop closure, thought to be essential for sequestration of the substrate, may be triggered by the formation of the carbanion or aci-carboxylate intermediates, whose charge distribution more closely mimics that of the sulphate ion found in the active-site region of the inactive ddeltac1. The 280s loop in ddeltac1 is in the closed conformation.
Figures
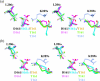
Similar articles
-
A duck delta1 crystallin double loop mutant provides insight into residues important for argininosuccinate lyase activity.Biochemistry. 2004 Sep 21;43(37):11672-82. doi: 10.1021/bi0489006. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15362851
-
Recovery of argininosuccinate lyase activity in duck delta1 crystallin.Biochemistry. 2005 Jun 28;44(25):9034-44. doi: 10.1021/bi050346s. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15966727
-
Structural studies of duck delta 1 and delta 2 crystallin suggest conformational changes occur during catalysis.Biochemistry. 2001 Mar 6;40(9):2732-42. doi: 10.1021/bi002272k. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11258884
-
Aspartase/fumarase superfamily: a common catalytic strategy involving general base-catalyzed formation of a highly stabilized aci-carboxylate intermediate.Biochemistry. 2012 May 29;51(21):4237-43. doi: 10.1021/bi300430j. Epub 2012 May 15. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 22551392 Review.
-
Intragenic complementation and the structure and function of argininosuccinate lyase.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000 Oct;57(11):1637-51. doi: 10.1007/pl00000646. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000. PMID: 11092456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Basis for the Catalytic Mechanism of Ethylenediamine- N, N'-disuccinic Acid Lyase, a Carbon-Nitrogen Bond-Forming Enzyme with a Broad Substrate Scope.Biochemistry. 2018 Jul 3;57(26):3752-3763. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00406. Epub 2018 May 18. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29741885 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Arginine from Ornithine in Maritime Pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.).Plants (Basel). 2020 Sep 27;9(10):1271. doi: 10.3390/plants9101271. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992504 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and heterologous expression of an epimerase and two lyases from iminodisuccinate-degrading bacteria.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Apr;72(4):2824-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2824-2828.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597988 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of Glu294 at the subunit interface is important for the activity and stability of goose delta-crystallin.Mol Vis. 2009 Nov 14;15:2358-63. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 19936305 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mutations in Malaysian patients with argininosuccinate lyase (ASL) deficiency.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019 Oct 24;21:100525. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100525. eCollection 2019 Dec. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31709144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piatigorsky J. Lens crystallins and their genes: diversity and tissue-specific expression. FASEB J. 1989;3:1933–1940. - PubMed
-
- Piatigorsky J., Kantorow M., Gopal-Srivastava R., Tomarev S. I. Recruitment of enzymes and stress proteins as lens crystallins. EXS. 1994;71:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Mori M., Matsubasa T., Amaya Y., Takiguchi M. Molecular evolution from argininosuccinate lyase to delta-crystallin. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1990;344:683–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

