Phosphonium compounds as new and specific inhibitors of bovine serum amine oxidase
- PMID: 15320876
- PMCID: PMC1134140
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20031883
Phosphonium compounds as new and specific inhibitors of bovine serum amine oxidase
Abstract
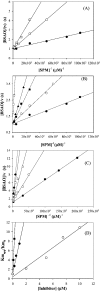
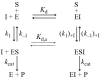
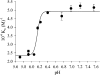
TPP+ (tetraphenylphosphonium ion) and its analogues were found to act as powerful competitive inhibitors of BSAO (bovine serum amine oxidase). The binding of this new class of inhibitors to BSAO was characterized by kinetic measurements. TPP+ can bind to the BSAO active site by hydrophobic and by coulombian interactions. The binding probably occurs in the region of the 'cation-binding site'[Di Paolo, Scarpa, Corazza, Stevanato and Rigo (2002) Biophys. J. 83, 2231-2239]. Under physiological conditions, the association constant of TPP+ for this site is higher than 10(6) M(-1), the change of enthalpy being the main free-energy term controlling binding. Analysis of the relationships between substrate structure and extent of inhibition by TPP+ reveals some new molecular features of the BSAO active site.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrostatic compared with hydrophobic interactions between bovine serum amine oxidase and its substrates.Biochem J. 2003 Apr 15;371(Pt 2):549-56. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021055. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12529179 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of dioxygen to non-metal sites in proteins: exploration of the importance of binding site size versus hydrophobicity in the copper amine oxidase from Hansenula polymorpha.Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 19;41(46):13637-43. doi: 10.1021/bi0204591. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12427025
-
Probing the mechanism of proton coupled electron transfer to dioxygen: the oxidative half-reaction of bovine serum amine oxidase.Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 8;37(36):12513-25. doi: 10.1021/bi981103l. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9730824
-
Inhibition and oxygen activation in copper amine oxidases.Acc Chem Res. 2015 May 19;48(5):1218-26. doi: 10.1021/ar500460z. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25897668 Review.
-
Inhibitors of plant copper amine oxidases.J Enzyme Inhib. 1998 Aug;13(5):311-25. doi: 10.3109/14756369809021478. J Enzyme Inhib. 1998. PMID: 9793836 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of buffer cations on interactions between mammalian copper-containing amine oxidases and their substrates.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007;114(6):733-41. doi: 10.1007/s00702-007-0680-1. Epub 2007 Mar 31. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007. PMID: 17401532
-
Reversible inhibition of copper amine oxidase activity by channel-blocking ruthenium(II) and rhenium(I) molecular wires.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 20;102(38):13451-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506336102. Epub 2005 Sep 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16157884 Free PMC article.
-
HPLC-UV assay for the evaluation of inhibitors of plasma amine oxidase using crude bovine plasma.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):144-149. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1524890. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30427224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knowles P. F., Dooley D. M. Amine Oxidases. In: Sigel H., Sigel A., editors. Metal Ions in Biological Systems, vol. 30. New York: Dekker; 1994. pp. 361–403.
-
- Padiglia A., Medda R., Bellelli A., Agostinelli E., Morpurgo L., Mondovì B., Finazzi-Agrò A., Floris G. The reductive and oxidative half-reactions and the role of copper ions in plant and mammalian copper-amine oxidases. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001;1:35–42.
-
- Mure M., Mills S. A., Klinman J. P. Catalytic mechanism of the topaquinone containing copper amine oxidases. Biochemistry. 2002;41:9269–9278. - PubMed
-
- McGuirl M. A., Dooley D. M. Copper-containing oxidases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999;3:138–144. - PubMed
-
- Duff A. P., Cohen A. E., Ellis P. J., Kuchar J. A., Langley D. B., Shepard E. M., Dooley D. M., Freeman H. C., Guss J. M. The crystal structure of Pichia pastoris lysyl oxidase. Biochemistry. 2003;42:15148–15157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

