SseK1 and SseK2 are novel translocated proteins of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 15322005
- PMCID: PMC517430
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5115-5125.2004
SseK1 and SseK2 are novel translocated proteins of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
Abstract
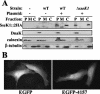
Salmonella enterica is a gram-negative, facultative intracellular pathogen that causes disease symptoms ranging from gastroenteritis to typhoid fever. A key virulence strategy is the translocation of bacterial effector proteins into the host cell, mediated by the type III secretion systems (TTSSs) encoded in Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI-1) and SPI-2. In S. enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2, we identified the protein products of STM4157 and STM2137 as novel candidate secreted proteins by comparison to known secreted proteins from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and Citrobacter rodentium. The STM4157 and STM2137 proteins, which we have designated SseK1 and SseK2, respectively, are 61% identical at the amino acid level and differ mainly in their N termini. Western analysis showed that in vitro accumulation and secretion of these proteins in serovar Typhimurium were affected by mutations in the two-component systems SsrA/B and PhoP/Q, which are key mediators of intracellular growth and survival. SPI-2 TTSS-dependent translocation of recombinant SseK1::Cya was evident at 9 h postinfection of epithelial cells, while translocation of SseK2::Cya was not detected until 21 h. Remarkably, the translocation signal for SseK1 was contained within the N-terminal 32 amino acids. Fractionation of infected epithelial cells revealed that following translocation SseK1 localizes to the host cytosol, which is unusual among the currently known Salmonella effectors. Phenotypic analysis of DeltasseK1, DeltasseK2, and DeltasseK1/DeltasseK2 mutants provided evidence for a role that was not critical during systemic infection. In summary, this work demonstrates that SseK1 and SseK2 are novel translocated proteins of serovar Typhimurium.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson, D. M., and O. Schneewind. 1997. A mRNA signal for the type III secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. Science 278:1140-1143. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1995. HilA is a novel OmpR/ToxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol. Microbiol. 18:715-727. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Brumell, J. H., S. Kujat-Choy, N. F. Brown, B. A. Vallance, L. A. Knodler, and B. B. Finlay. 2003. SopD2 is a novel type III secreted effector of Salmonella typhimurium that targets late endocytic compartments upon delivery into host cells. Traffic 4:36-48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

