Mycobacterium tuberculosis triggers apoptosis in peripheral neutrophils involving toll-like receptor 2 and p38 mitogen protein kinase in tuberculosis patients
- PMID: 15322009
- PMCID: PMC517458
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5150-5158.2004
Mycobacterium tuberculosis triggers apoptosis in peripheral neutrophils involving toll-like receptor 2 and p38 mitogen protein kinase in tuberculosis patients
Abstract
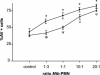
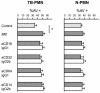
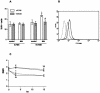
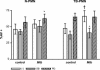
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis display bactericidal responses and produce inflammatory proteins. This PMN-mediated inflammatory response is regulated by an activation of the apoptotic program, which collaborates to avoid tissue injury. In vitro, circulating PMN from patients with tuberculosis (TB) show an increased spontaneous apoptosis, and M. tuberculosis-induced activation accelerates the PMN apoptosis. In this study, we evaluated the mechanisms involved in spontaneous and M. tuberculosis-induced apoptosis. We demonstrate that apoptosis of PMN is not induced by lipoarabinomannan or by a whole-cell lysate of M. tuberculosis and that neither tumor necrosis factor alpha nor CD11b, CD14, and Fcgamma receptors are involved. Apoptosis of PMN from patients with active TB (TB-PMN) is induced by the interaction with the whole M. tuberculosis via Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), and, in contrast to spontaneous apoptosis, it involves the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. These results correlate with a high expression of phosphorylated p38 (p-p38) in circulating TB-PMN and with the ability of M. tuberculosis to induce in vitro the expression of p-p38 in PMN. Therefore, when the bacterial burden is low, TB-PMN could be detecting nonopsonized M. tuberculosis via TLR2, leading to the activation of the p38 MAPK pathway, which in turn would induce PMN activation and apoptosis. This mechanism needs further confirmation at the site of infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced activation accelerates apoptosis in peripheral blood neutrophils from patients with active tuberculosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002 Nov;27(5):583-92. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2002-0038OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12397018
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced gamma interferon production by natural killer cells requires cross talk with antigen-presenting cells involving Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and the mannose receptor in tuberculous pleurisy.Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5325-37. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00381-07. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17709420 Free PMC article.
-
TLR5-mediated activation of p38 MAPK regulates epithelial IL-8 expression via posttranscriptional mechanism.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Aug;285(2):G282-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00503.2002. Epub 2003 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12702497
-
Neutrophil apoptosis in the context of tuberculosis infection.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015 Jul;95(4):359-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2015. PMID: 25864404 Review.
-
Neutrophils in tuberculosis--first line of defence or booster of disease and targets for host-directed therapy?Pathog Dis. 2016 Apr;74(3):ftw012. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw012. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 26903072 Review.
Cited by
-
Bystander macrophage apoptosis after Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra infection.Infect Immun. 2008 Jan;76(1):351-60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00614-07. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 17954721 Free PMC article.
-
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis early secreted antigenic target of 6 kDa inhibits T cell interferon-γ production through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 8;286(27):24508-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.234062. Epub 2011 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21586573 Free PMC article.
-
Defective functions of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in patients with common variable immunodeficiency.Immunol Res. 2014 Oct;60(1):69-76. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8555-7. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24981124
-
ESX-1-induced apoptosis during mycobacterial infection: to be or not to be, that is the question.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Dec 4;3:88. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00088. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24364000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Delays Neutrophil Apoptosis and Stimulates the Release of a Prosurvival Secretome.Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 25;8:1185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01185. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28993776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aga, E., D. M. Katschinski, G. Van Zandvergen, H. Laufs, B. Hansen, K. Müller, W. Solbach, and T. Laskay. 2002. Inhibition of the spontaneous apoptosis of neutrophil granulocytes by the intracellular parasite Leishmania major. J. Immunol. 169:898-905. - PubMed
-
- Alemán, M., M. Beigier-Bompadre, C. Borghetti, S. de la Barrera, E. Abbate, M. Isturiz, and M. C. Sasiain. 2001. Activation of peripheral blood neutrophils from patients with active advanced tuberculosis. Clin. Immunol. 100:87-95. - PubMed
-
- Alemán, M., A. García, M. Saab, S. de la Barrera, M. Finiazs, E. Abbate, and M. C. Sasiain. 2002. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced activation accelerates apoptosis in peripheral blood neutrophils from patients with active tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 27:583-592. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis, A. O., R. B. Yang, M. R. Mark, S. Suggett, B. Devaux, J. D. Radolf, G. R. Klimpel, P. Godowsky, and A. Zychlinsky. 1999. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor 2. Science 285:736-739. - PubMed
-
- Appelberg, R. 1992. Mycobacterial infection primes T cells and macrophages for enhanced recruitment of neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 57:472-477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

