Helicobacter pylori infection targets adherens junction regulatory proteins and results in increased rates of migration in human gastric epithelial cells
- PMID: 15322013
- PMCID: PMC517469
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5181-5192.2004
Helicobacter pylori infection targets adherens junction regulatory proteins and results in increased rates of migration in human gastric epithelial cells
Abstract
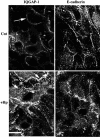
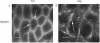
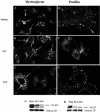
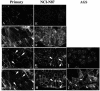
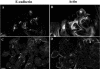
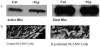
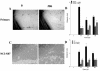
The human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori attaches to antral epithelial cells in vivo. Cultured human antral epithelial cells, AGS and NCI-N87 cell lines, were grown in the absence or presence of H. pylori and compared with respect to gene transcript levels, protein expression, organization of the actin cytoskeleton, and the regulation of cell migration. The Clontech Neurobiology array detected differentially expressed transcripts, while Western blots were used to investigate related changes in protein levels. Infection with H. pylori consistently upregulated annexin II, S100 A7, Rho-GTP, and IQGAP-1, whereas SSTR-1 was downregulated upon H. pylori infection. In the adherens junction, E-cadherin and IQGAP-1 were translocated from the plasma membrane to intracellular vesicles. The primary and NCI-N87 cells were similar with respect to cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion and cell migratory behavior; in contrast the AGS cells were significantly different from the primary gastric epithelial cell preparations, and thus caution must be used when using this cell line for studies of gastric disease. These studies demonstrate a correlation between H. pylori infection and alterations to epithelial cell adhesion molecules, including increased levels of Rho-GTP and cell migration. These data indicate that destabilizing epithelial cell adherence is one of the factors increasing the risk of H. pylori-infected individuals developing gastric cancer.
Figures
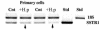



Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 2-mediated gene expression in epithelial cells during Helicobacter pylori infection.Helicobacter. 2005 Jun;10(3):193-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2005.00311.x. Helicobacter. 2005. PMID: 15904477
-
CagA-independent disruption of adherence junction complexes involves E-cadherin shedding and implies multiple steps in Helicobacter pylori pathogenicity.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Oct 1;313(16):3459-71. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.07.015. Epub 2007 Jul 24. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17692843
-
Gene expression and protein profiling of AGS gastric epithelial cells upon infection with Helicobacter pylori.Proteomics. 2005 Oct;5(15):3902-18. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200401240. Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 16145711
-
Adherens junctions as targets of microorganisms: a focus on Helicobacter pylori.FEBS Lett. 2013 Jan 31;587(3):259-65. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.12.008. Epub 2012 Dec 19. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23262219 Review.
-
Exploiting the Gastric Epithelial Barrier: Helicobacter pylori's Attack on Tight and Adherens Junctions.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;400:195-226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50520-6_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28124155 Review.
Cited by
-
Alkannin inhibits growth and invasion of glioma cells C6 through IQGAP/mTOR signal pathway.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):5287-94. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131103 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori dysregulation of gastric epithelial tight junctions by urease-mediated myosin II activation.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jan;136(1):236-46. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.011. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 18996125 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that modulate disease risk.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Oct;23(4):713-39. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00011-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20930071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Middle Fragment of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Actin Rearrangement and Triggers Its Own Uptake into Gastric Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jul 28;9(8):237. doi: 10.3390/toxins9080237. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28788072 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori chemotaxis modulates inflammation and bacterium-gastric epithelium interactions in infected mice.Infect Immun. 2007 Aug;75(8):3747-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00082-07. Epub 2007 May 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17517875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babiychuk, E. B., K. Monastyrskaya, F. C. Burkhard, S. Wray, and A. Draeger. 2002. Modulating signaling events in smooth muscle: cleavage of annexin 2 abolishes its binding to lipid rafts. FASEB J. 16:1177-1184. - PubMed
-
- Barber, D. L., A. M. J. Buchan, C.-Y. Lin, and J. Choi J. 2000. Somatostatin acting at SSTR1 subtype inhibits activation of Rho and actin stress fibre formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 11:100a. (Abstract.)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

