Contribution of the major secreted yops of Yersinia enterocolitica O:8 to pathogenicity in the mouse infection model
- PMID: 15322017
- PMCID: PMC517446
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5227-5234.2004
Contribution of the major secreted yops of Yersinia enterocolitica O:8 to pathogenicity in the mouse infection model
Abstract
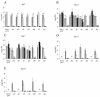
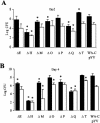
Pathogenic yersiniae (Yersinia pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. enterocolitica) harbor a 70-kb virulence plasmid (pYV) that encodes a type III secretion system and a set of at least six effector proteins (YopH, YopO, YopP, YopE, YopM, and YopT) that are injected into the host cell cytoplasm. Yops (Yersinia outer proteins) disturb the dynamics of the cytoskeleton, inhibit phagocytosis by macrophages, and downregulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines, which makes it possible for yersiniae to multiply extracellularly in lymphoid tissue. Y. enterocolitica serotype O:8 belongs to the highly mouse-pathogenic group of yersiniae in contrast to Y. enterocolitica serotype O:9. However, there has been no systematic study of the contribution of Yops to the pathogenicity of Y. enterocolitica O:8 in mice. We generated a set of yop gene deletion mutants of Y. enterocolitica O:8 by using the novel Red cloning procedure. We subsequently analyzed the contribution of yopH, -O, -P, -E, -M, -T, and -Q deletions to pathogenicity after oral and intravenous infection of mice. Here we showed for the first time that a DeltayopT deletion mutant colonizes mouse tissues to a greater extent than the parental strain. The DeltayopO, DeltayopP, and DeltayopE mutants were only slightly attenuated after oral infection since they were still able to colonize the spleen and liver and cause systemic infection. The DeltayopO mutant was lethal for mice, whereas DeltayopP and DeltayopE mutants were successfully eliminated from the spleen and liver 2 weeks after infection. In contrast the DeltayopH, DeltayopM, and DeltayopQ mutants were highly attenuated and not able to colonize the spleen and liver on any of the days tested. The DeltayopH, DeltayopO, DeltayopP, DeltayopE, DeltayopM, and DeltayopQ mutants had only modest defects in the colonization of the small intestine and Peyer's patches. The DeltayopE mutant was eliminated from the small intestine 3 weeks after infection, whereas the DeltayopH, DeltayopP, DeltayopM, and DeltayopQ mutants continued to colonize the small intestine at this time.
Figures


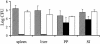
Similar articles
-
Yersinia enterocolitica YopH-Deficient Strain Activates Neutrophil Recruitment to Peyer's Patches and Promotes Clearance of the Virulent Strain.Infect Immun. 2016 Oct 17;84(11):3172-3181. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00568-16. Print 2016 Nov. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27550935 Free PMC article.
-
The proinflammatory response induced by wild-type Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection inhibits survival of yop mutants in the gastrointestinal tract and Peyer's patches.Infect Immun. 2006 Mar;74(3):1516-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1516-1527.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16495522 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of chaperone-dependent Yop secretion/translocation and effector function using a mini-virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica.Int J Med Microbiol. 2003 Jun;293(2-3):167-77. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00251. Int J Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12868653
-
Yersinia outer proteins: role in modulation of host cell signaling responses and pathogenesis.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:69-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.59.030804.121320. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15847602 Review.
-
Modulation of Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton by Yersinia outer proteins (Yops).Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 Sep;291(4):269-76. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00130. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11680787 Review.
Cited by
-
Histamine signaling through the H(2) receptor in the Peyer's patch is important for controlling Yersinia enterocolitica infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 13;103(24):9268-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510414103. Epub 2006 May 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16717182 Free PMC article.
-
YopH inhibits early pro-inflammatory cytokine responses during plague pneumonia.BMC Immunol. 2010 Jun 16;11:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-29. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20565713 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of specific sequence motif of YopN of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis required for systemic infection.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):10-25. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1551709. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 30488778 Free PMC article.
-
LIGHT-HVEM Signaling in Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets Protects Against Enteric Bacterial Infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2018 Aug 8;24(2):249-260.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.07.008. Cell Host Microbe. 2018. PMID: 30092201 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia effector YopO uses actin as bait to phosphorylate proteins that regulate actin polymerization.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;22(3):248-55. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2964. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25664724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, A., N. Bottini, S. Bruckner, S. Rahmouni, S. Williams, S. P. Schoenberger, and T. Mustelin. 2003. Lck dephosphorylation at Y394 and inhibition of T-cell antigen receptor signaling by Yersinia phosphatase YopH. J. Biol. Chem. 6:4922-4928. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates, Brooklyn, N.Y.
-
- Autenrieth, I. B., E. Bohn, J. H. Ewald, and J. Heesemann. 1995. Deferoxamine B but not deferoxamine G1 inhibits cytokine production in murine bone marrow macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 172:490-496. - PubMed
-
- Autenrieth, I. B., R. Reissbrodt, E. Saken, R. Berner, U. Vogel, W. Rabsch, and J. Heesemann. 1994. Desferrioxamine-promoted virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica in mice depends on both desferrioxamine type and mouse strain. J. Infect. Dis. 169:562-567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

