Long-range allosteric transitions in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
- PMID: 15322282
- PMCID: PMC2280008
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.04822704
Long-range allosteric transitions in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
Abstract
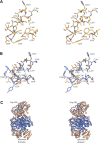
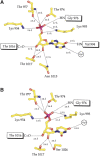
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase plays a key role in both pyrimidine and arginine biosynthesis by catalyzing the production of carbamoyl phosphate from one molecule of bicarbonate, two molecules of MgATP, and one molecule of glutamine. The enzyme from Escherichia coli consists of two polypeptide chains referred to as the small and large subunits, which contain a total of three separate active sites that are connected by an intramolecular tunnel. The small subunit harbors one of these active sites and is responsible for the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate and ammonia. The large subunit binds the two required molecules of MgATP and is involved in assembling the final product. Compounds such as L-ornithine, UMP, and IMP allosterically regulate the enzyme. Here, we report the three-dimensional structure of a site-directed mutant protein of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase from E. coli, where Cys 248 in the small subunit was changed to an aspartate. This residue was targeted for a structural investigation because previous studies demonstrated that the partial glutaminase activity of the C248D mutant protein was increased 40-fold relative to the wild-type enzyme, whereas the formation of carbamoyl phosphate using glutamine as a nitrogen source was completely abolished. Remarkably, although Cys 248 in the small subunit is located at approximately 100 A from the allosteric binding pocket in the large subunit, the electron density map clearly revealed the presence of UMP, although this ligand was never included in the purification or crystallization schemes. The manner in which UMP binds to carbamoyl phosphate synthetase is described.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Site-directed mutagenesis of the regulatory domain of Escherichia coli carbamoyl phosphate synthetase identifies crucial residues for allosteric regulation and for transduction of the regulatory signals.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jun 16;299(4):979-91. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3794. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10843852
-
Regulatory changes in the control of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase induced by truncation and mutagenesis of the allosteric binding domain.Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 24;34(42):13920-7. doi: 10.1021/bi00042a025. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 7577987
-
Allosteric dominance in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.Biochemistry. 1999 Feb 2;38(5):1394-401. doi: 10.1021/bi982097w. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 9931004
-
The amidotransferase family of enzymes: molecular machines for the production and delivery of ammonia.Biochemistry. 1999 Jun 22;38(25):7891-9. doi: 10.1021/bi990871p. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10387030 Review.
-
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: a crooked path from substrates to products.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998 Oct;2(5):624-32. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(98)80094-x. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998. PMID: 9818189 Review.
Cited by
-
Resolving the fluorescence response of Escherichia coli carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: mapping intra- and intersubunit conformational changes.Biochemistry. 2007 Jan 16;46(2):387-97. doi: 10.1021/bi061642n. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17209549 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric regulation of CAD modulates de novo pyrimidine synthesis during the cell cycle.Nat Metab. 2023 Feb;5(2):277-293. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00735-9. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 36747088 Free PMC article.
-
Eight Kinetically Stable but Thermodynamically Activated Molecules that Power Cell Metabolism.Chem Rev. 2018 Feb 28;118(4):1460-1494. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00510. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29272116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-isobutylmethylxanthine inhibits hepatic urea synthesis: protection by agmatine.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 30;283(22):15063-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800163200. Epub 2008 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18375388 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of carbamoylphosphate synthesis in Escherichia coli: an amazing metabolite at the crossroad of arginine and pyrimidine biosynthesis.Amino Acids. 2018 Dec;50(12):1647-1661. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2654-z. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Amino Acids. 2018. PMID: 30238253 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boettcher, B. and Meister, A. 1981. Conversion of UMP, an allosteric inhibitor of carbamyl phosphate synthetase, to an activator by modification of the UMP ribose moiety. J. Biol. Chem. 256 5977–5980. - PubMed
-
- ———. 1982. Regulation of Escherichia coli carbamyl phosphate synthetase. Evidence for overlap of the allosteric nucleotide binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 257 13971–13976. - PubMed
-
- Braxton, B.L., Mullins, L.S., Raushel, F.M., and Reinhart, G.D. 1992. Quantifying the allosteric properties of Escherichia coli carbamyl phosphate synthetase: Determination of thermodynamic linked-function parameters in an ordered kinetic mechanism. Biochemistry 31 2309–2316. - PubMed
-
- Braxton, B.L., Mullins, L.S., Raushel, F.M., and Reinhart, G.D. 1996. Allosteric effects of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase from Escherichia coli are entropy-driven. Biochemistry 35 11918–11924. - PubMed
-
- Braxton, B.L., Mullins, L.S., Raushel, F.M., and Reinhart, G.D. 1999. Allosteric dominance in carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Biochemistry 38 1394–1401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

