Mutation history of the roma/gypsies
- PMID: 15322984
- PMCID: PMC1182047
- DOI: 10.1086/424759
Mutation history of the roma/gypsies
Abstract
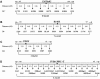
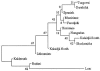
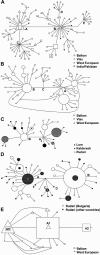
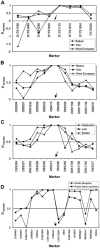
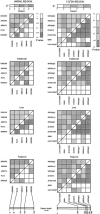
The 8-10 million European Roma/Gypsies are a founder population of common origins that has subsequently split into multiple socially divergent and geographically dispersed Gypsy groups. Unlike other founder populations, whose genealogy has been extensively documented, the demographic history of the Gypsies is not fully understood and, given the lack of written records, has to be inferred from current genetic data. In this study, we have used five disease loci harboring private Gypsy mutations to examine some missing historical parameters and current structure. We analyzed the frequency distribution of the five mutations in 832-1,363 unrelated controls, representing 14 Gypsy populations, and the diversification of chromosomal haplotypes in 501 members of affected families. Sharing of mutations and high carrier rates supported a strong founder effect, and the identity of the congenital myasthenia 1267delG mutation in Gypsy and Indian/Pakistani chromosomes provided the best evidence yet of the Indian origins of the Gypsies. However, dramatic differences in mutation frequencies and haplotype divergence and very limited haplotype sharing pointed to strong internal differentiation and characterized the Gypsies as a founder population comprising multiple subisolates. Using disease haplotype coalescence times at the different loci, we estimated that the entire Gypsy population was founded approximately 32-40 generations ago, with secondary and tertiary founder events occurring approximately 16-25 generations ago. The existence of multiple subisolates, with endogamy maintained to the present day, suggests a general approach to complex disorders in which initial gene mapping could be performed in large families from a single Gypsy group, whereas fine mapping would rely on the informed sampling of the divergent subisolates and searching for the shared genomic region that displays the strongest linkage disequilibrium with the disease.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Genome View, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mapview/map_search.cgi?taxid=9606 (for the deCODE genetic map)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for HMSNL, CCFDN, CMS, LGMD2C, and galactokinase deficiency)
References
-
- Abicht A, Stucka R, Karcagi V, Herczegfalvi A, Horvath R, Mortier W, Schara U, Ramaekers V, Jost W, Brunner J, Janssen G, Seidel U, Schlotter B, Muller-Felber W, Pongratz D, Rudel R, Lochmuller H (1999) A common mutation (epsilon1267delG) in congenital myasthenic patients of Gypsy ethnic origin. Neurology 53:1564–1569 - PubMed
-
- Angelicheva D, Turnev I, Dye D, Chandler D, Thomas PK, Kalaydjieva L (1999) Congenital cataracts facial dysmorphism neuropathy (CCFDN) syndrome: a novel developmental disorder in Gypsies maps to 18qter. Eur J Hum Genet 7:560–566 - PubMed
-
- Angius A, Bebbere D, Petretto E, Falchi M, Forabosco P, Maestrale B, Casu G, Persico I, Melis PM, Pirastu M (2002) Not all isolates are equal: linkage disequilibrium analysis on Xq13.3 reveals different patterns in Sardinian sub-populations. Hum Genet 111:9–15 10.1007/s00439-002-0753-z - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

