Azithromycin inhibits MUC5AC production induced by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer N-(3-Oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone in NCI-H292 Cells
- PMID: 15328111
- PMCID: PMC514791
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.9.3457-3461.2004
Azithromycin inhibits MUC5AC production induced by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer N-(3-Oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone in NCI-H292 Cells
Abstract
The features of chronic airway diseases, including chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis, and diffuse panbronchiolitis, include chronic bacterial infection and airway obstruction by mucus. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most common pathogens in chronic lung infection, and quorum-sensing systems contribute to the pathogenesis of this disease. The quorum-sensing signal molecule [N-(3-oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone (3O-C(12)-HSL)] not only regulates bacterial virulence but also is associated with the immune response. In this study, we investigated whether 3O-C(12)-HSL could stimulate the production of a major mucin core protein, MUC5AC. The effect of a macrolide on MUC5AC production was also studied. 3O-C(12)-HSL induced NCI-H292 cells to express MUC5AC at both the mRNA and the protein levels in time- and dose-dependent manners. A 15-membered macrolide, azithromycin, inhibited MUC5AC production that was activated by 3O-C(12)-HSL. 3O-C(12)-HSL induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and I-kappa B phosphorylation in cells, and this induction was suppressed by azithromycin. 3O-C(12)-HSL-induced MUC5AC production was blocked by the ERK pathway inhibitor PD98059. Our findings suggest that the P. aeruginosa autoinducer 3O-C(12)-HSL contributes to excessive mucin production in chronic bacterial infection. Azithromycin seems to reduce this mucin production by interfering with intracellular signal transduction.
Figures
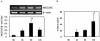

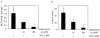

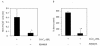
Similar articles
-
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone stimulates phagocytic activity in human macrophages through the p38 MAPK pathway.Microbes Infect. 2005 Dec;7(15):1512-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.05.012. Epub 2005 Jul 1. Microbes Infect. 2005. PMID: 16039899
-
The Pseudomonas autoinducer N-(3-oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone induces cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 production in human lung fibroblasts: implications for inflammation.J Immunol. 2002 Sep 1;169(5):2636-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.5.2636. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12193735
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing molecule N-(3 oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone disrupts epithelial barrier integrity of Caco-2 cells.FEBS Lett. 2006 Dec 22;580(30):6921-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.11.057. Epub 2006 Dec 4. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 17157842
-
Molecular radio jamming: autoinducer analogs.Chem Biol. 2003 Jan;10(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(03)00005-x. Chem Biol. 2003. PMID: 12573691 Review.
-
P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003 Feb;6(1):56-60. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(03)00008-0. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12615220 Review.
Cited by
-
Clarithromycin delays progression of bronchial epithelial cells from G1 phase to S phase and delays cell growth via extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase suppression.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 May;50(5):1738-44. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.5.1738-1744.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16641444 Free PMC article.
-
Azithromycin use in patients with cystic fibrosis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015 Jun;34(6):1071-9. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2347-4. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25686729 Review.
-
The front line of enteric host defense against unwelcome intrusion of harmful microorganisms: mucins, antimicrobial peptides, and microbiota.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):315-37. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.2.315-337.2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16614252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Azithromycin in viral infections.Rev Med Virol. 2021 Mar;31(2):e2163. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2163. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Rev Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32969125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The value of macrolides in the adjuvant treatment of pulmonary fibrosis: maybe a panacea.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666251346108. doi: 10.1177/17534666251346108. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40554453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charlton, T. S., R. de Nys, A. Netting, N. Kumar, M. Hentzer, M. Givskov, and S. Kjelleberg. 2000. A novel and sensitive method for the quantification of N-3-oxoacyl homoserine lactones using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: application to a model bacterial biofilm. Environ. Microbiol. 2:530-541. - PubMed
-
- Dabbagh, K., K. Takeyama, H. M. Lee, I. F. Ueki, J. A. Lausier, and J. A. Nadel. 1999. IL-4 induces mucin gene expression and goblet cell metaplasia in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 162:6233-6237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

