The AcrAB-TolC pump is involved in macrolide resistance but not in telithromycin efflux in Enterobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15328143
- PMCID: PMC514773
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.9.3621-3624.2004
The AcrAB-TolC pump is involved in macrolide resistance but not in telithromycin efflux in Enterobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli
Abstract
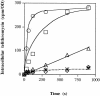
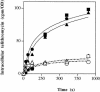
The role of the AcrAB-TolC pump in macrolide and ketolide susceptibility in Escherichia coli and Enterobacter aerogenes was studied. Efflux pump inhibitor restored erythromycin, clarithromycin, and telithromycin susceptibilities to multidrug-resistant isolates. No modification of telithromycin accumulation was detected in E. aerogenes acrAB or tolC derivatives compared to that in the parental strain. Two independent efflux pumps, inhibited by phenylalanine arginine beta-naphthylamide, expel macrolides and telithromycin in E. aerogenes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Boosting the Antibacterial Activity of Azithromycin on Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli by Efflux Pump Inhibition Coupled with Outer Membrane Permeabilization Induced by Phenylalanine-Arginine β-Naphthylamide.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 12;24(10):8662. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108662. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240007 Free PMC article.
-
The AcrAB-TolC efflux pump contributes to multidrug resistance in the nosocomial pathogen Enterobacter aerogenes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Aug;46(8):2640-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.8.2640-2643.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12121946 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of macrolide resistance in Campylobacter: role of efflux pumps and target mutations.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005 Sep;56(3):491-7. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki253. Epub 2005 Jul 29. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16055509
-
Properties of AdeABC and AdeIJK efflux systems of Acinetobacter baumannii compared with those of the AcrAB-TolC system of Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Dec;58(12):7250-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03728-14. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 25246403 Free PMC article.
-
Quinoline derivatives as promising inhibitors of antibiotic efflux pump in multidrug resistant Enterobacter aerogenes isolates.Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Jul;7(7):843-7. doi: 10.2174/138945006777709557. Curr Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16842215 Review.
Cited by
-
Cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and analysis of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump of Enterobacter cloacae and determination of its involvement in antibiotic resistance in a clinical isolate.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Sep;51(9):3247-53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00072-07. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17638702 Free PMC article.
-
The intrinsic resistome of bacterial pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2013 Apr 30;4:103. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00103. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23641241 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic exchange of multidrug efflux pumps among two enterobacterial species with distinctive ecological Niches.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 Feb;10(2):629-645. doi: 10.3390/ijms10020629. Epub 2009 Feb 19. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19333425 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Bacterial Drug Efflux Pumps via Phyto-Therapeutics to Combat Threatening Antimicrobial Resistance.Front Microbiol. 2018 Dec 10;9:2990. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02990. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30619113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinically relevant chromosomally encoded multidrug resistance efflux pumps in bacteria.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Apr;19(2):382-402. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.2.382-402.2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16614254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bryskier, A. 2000. Ketolides-telithromycin, an example of a new class of antibacterial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 6:661-669. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein, E. J., D. M. Citron, C. V. Merriam, Y. Warren, K. L. Tyrrel, and H. Fernandez. 2003. In vitro activities of telithromycin and 10 oral agents against aerobic and anaerobic pathogens isolated from antral puncture specimens from patients with sinusitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:1963-1967. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

