Concomitant use of tamoxifen with radiotherapy enhances subcutaneous breast fibrosis in hypersensitive patients
- PMID: 15328527
- PMCID: PMC2409893
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602146
Concomitant use of tamoxifen with radiotherapy enhances subcutaneous breast fibrosis in hypersensitive patients
Abstract
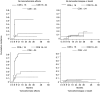
Concomitant use of adjuvant tamoxifen (TAM) and radiation therapy (RT) is not widely accepted. We aim to assess whether this treatment is associated with an increased risk of developing subcutaneous fibrosis after conservative or radical surgery in breast cancer patients. We analysed 147 women with breast cancer treated with adjuvant RT, and who were included in the KFS 00539-9-1997/SKL 00778-2-1999 prospective study aimed at evaluating the predictive value of CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocyte apoptosis for the development of radiation-induced late effects. TAM (20 mg day(-1)) with concomitant RT was prescribed in 90 hormone receptor-positive patients. There was a statistically significant difference in terms of complication-relapse-free survival (CRFS) rates at 3 years, 48% (95% CI 37.2-57.6%) vs 66% (95% CI 49.9-78.6%) and complication-free survival (CFS) rates at 2 years, 51% (95% CI 40-61%) vs 80% (95% CI 67-89%) in the TAM and no-TAM groups, respectively. In each of these groups, the CRFS rates were significantly lower for patients with low levels of CD8 radiation-induced apoptosis, 20% (95% CI 10-31.9%), 66% (95% CI 51.1-77.6%), and 79% (95% CI 55-90.9%) for CD8 </=16, 16-24, and >24%, respectively. Similar results were observed for the CFS rates. The concomitant use of TAM with RT is significantly associated with an increased incidence of grade 2 or greater subcutaneous fibrosis; therefore, caution is needed for radiosensitive patients.
Figures
References
-
- Azria D, Larbouret C, Cunat S, Romieu G, Evans D, Bastie A, Pujol P, Dubois JB, Pelegrin A (2003) Letrozole (Femara®) sensitises breast cancer cells to gamma irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 57: 255–256 - PubMed
-
- Barber JB, Burrill W, Spreadborough AR, Levine E, Warren C, Kiltie AE, Roberts SA, Scott D (2000) Relationship between in vitro chromosomal radiosensitivity of peripheral blood lymphocytes and the expression of normal tissue damage following radiotherapy for breast cancer. Radiother Oncol 55: 179–186 - PubMed
-
- Baum M, Budzar AU, Cuzick J, Forbes J, Houghton JH, Klijn JG, Sahmoud T (2002) Anastrozole alone or in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone for adjuvant treatment of postmenopausal women with early breast cancer: first results of the ATAC randomised trial. Lancet 359: 2131–2139 - PubMed
-
- Beadle GF, Silver B, Botnick L, Hellman S, Harris JR (1984) Cosmetic results following primary radiation therapy for early breast cancer. Cancer 54: 2911–2918 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials