The Rab5 effector Rabankyrin-5 regulates and coordinates different endocytic mechanisms
- PMID: 15328530
- PMCID: PMC514490
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020261
The Rab5 effector Rabankyrin-5 regulates and coordinates different endocytic mechanisms
Abstract
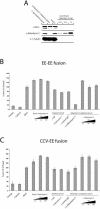
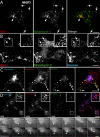
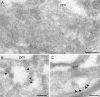
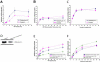
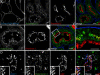
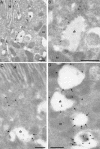
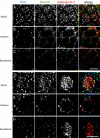
The small GTPase Rab5 is a key regulator of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. On early endosomes, within a spatially restricted domain enriched in phosphatydilinositol-3-phosphate [PI(3)P], Rab5 coordinates a complex network of effectors that functionally cooperate in membrane tethering, fusion, and organelle motility. Here we discovered a novel PI(3)P-binding Rab5 effector, Rabankyrin-5, which localises to early endosomes and stimulates their fusion activity. In addition to early endosomes, however, Rabankyrin-5 localises to large vacuolar structures that correspond to macropinosomes in epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Overexpression of Rabankyrin-5 increases the number of macropinosomes and stimulates fluid-phase uptake, whereas its downregulation inhibits these processes. In polarised epithelial cells, this function is primarily restricted to the apical membrane. Rabankyrin-5 localises to large pinocytic structures underneath the apical surface of kidney proximal tubule cells, and its overexpression in polarised Madin-Darby canine kidney cells stimulates apical but not basolateral, non-clathrin-mediated pinocytosis. In demonstrating a regulatory role in endosome fusion and (macro)pinocytosis, our studies suggest that Rab5 regulates and coordinates different endocytic mechanisms through its effector Rabankyrin-5. Furthermore, its active role in apical pinocytosis in epithelial cells suggests an important function of Rabankyrin-5 in the physiology of polarised cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
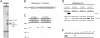


Similar articles
-
Rab5a is a common component of the apical and basolateral endocytic machinery in polarized epithelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5061-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5061. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 8197185 Free PMC article.
-
Rab5 regulates motility of early endosomes on microtubules.Nat Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;1(6):376-82. doi: 10.1038/14075. Nat Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10559966
-
EEA1 links PI(3)K function to Rab5 regulation of endosome fusion.Nature. 1998 Jul 30;394(6692):494-8. doi: 10.1038/28879. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9697774
-
[Effectors of GTPase Rab5 in endocytosis and signal transduction].Postepy Biochem. 2009;55(2):171-80. Postepy Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19824473 Review. Polish.
-
Vps9 domain-containing proteins: activators of Rab5 GTPases from yeast to neurons.Trends Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;16(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.11.001. Epub 2005 Dec 2. Trends Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16330212 Review.
Cited by
-
Yersinia entry into host cells requires Rab5-dependent dephosphorylation of PI(4,5)P₂ and membrane scission.Cell Host Microbe. 2012 Feb 16;11(2):117-28. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.010. Cell Host Microbe. 2012. PMID: 22341461 Free PMC article.
-
The redox sensor TXNL1 plays a regulatory role in fluid phase endocytosis.PLoS One. 2007 Nov 7;2(11):e1144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001144. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17987124 Free PMC article.
-
A dileucine motif in the COOH-terminal domain of NKCC1 targets the cotransporter to the plasma membrane.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr 1;316(4):C545-C558. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00023.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30865516 Free PMC article.
-
Virus entry by macropinocytosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 May;11(5):510-20. doi: 10.1038/ncb0509-510. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19404330 Review.
-
Cumulative lifetime maternal stress and epigenome-wide placental DNA methylation in the PRISM cohort.Epigenetics. 2018;13(6):665-681. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2018.1497387. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 30001177 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

