Unused natural variation can lift yield barriers in plant breeding
- PMID: 15328532
- PMCID: PMC514488
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020245
Unused natural variation can lift yield barriers in plant breeding
Abstract
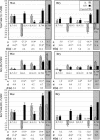
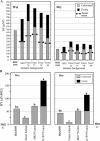
Natural biodiversity is an underexploited sustainable resource that can enrich the genetic basis of cultivated plants with novel alleles that improve productivity and adaptation. We evaluated the progress in breeding for increased tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) yield using genotypes carrying a pyramid of three independent yield-promoting genomic regions introduced from the drought-tolerant green-fruited wild species Solanum pennellii. Yield of hybrids parented by the pyramided genotypes was more than 50% higher than that of a control market leader variety under both wet and dry field conditions that received 10% of the irrigation water. This demonstration of the breaking of agricultural yield barriers provides the rationale for implementing similar strategies for other agricultural organisms that are important for global food security.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bernacchi D, Beck-Bunn T, Emmatty D, Eshed Y, Inai S, et al. Advanced backcross QTL analysis of tomato. II. Evaluation of near-isogenic lines carrying single-donor introgressions for desirable wild QTL-alleles derived from Lycopersicon hirsutum and L. pimpinellifolium . Theor Appl Genet. 1998;97:170–180.
-
- Bessey CE. American Breeders' Association II; 1906. Crop improvement by utilizing wild species; pp. 112–118.
-
- Concibido VC, La Vallee B, Mclaird P, Pineda N, Meyer J, et al. Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for yield from Glycine soja into commercial soybean cultivars. Theor Appl Genet. 2003;106:575–582. - PubMed
-
- Dudley JW, Moll RH. Interpretation and use of estimates of heritability and genetic variances in plant breeding. Crop Sci. 1969;9:257–262.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

