A requirement for MCM7 and Cdc45 in chromosome unwinding during eukaryotic DNA replication
- PMID: 15329670
- PMCID: PMC517609
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600369
A requirement for MCM7 and Cdc45 in chromosome unwinding during eukaryotic DNA replication
Abstract
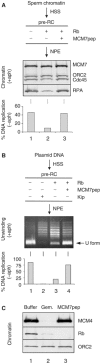
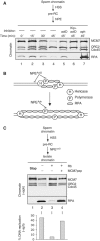
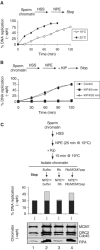
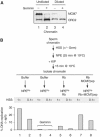
In vertebrates, MCM2-7 and Cdc45 are required for DNA replication initiation, but it is unknown whether they are also required for elongation, as in yeast. Moreover, although MCM2-7 is a prime candidate for the eukaryotic replicative DNA helicase, a demonstration that MCM2-7 unwinds DNA during replication is lacking. Here, we use Xenopus egg extracts to investigate the roles of MCM7 and Cdc45 in DNA replication. A fragment of the retinoblastoma protein, Rb(1-400), was used to neutralize MCM7, and antibodies were used to neutralize Cdc45. When added immediately after origin unwinding, or after significant DNA synthesis, both inhibitors blocked further DNA replication, indicating that MCM7 and Cdc45 are required throughout replication elongation in vertebrates. We next exploited the fact that inhibition of DNA polymerase by aphidicolin causes extensive chromosome unwinding, likely due to uncoupling of the replicative DNA helicase. Strikingly, Rb(1-400) and Cdc45 antibodies both abolished unwinding by the uncoupled helicase. These results provide new support for the model that MCM2-7 is the replicative DNA helicase, and they indicate that Cdc45 functions as a helicase co-factor.
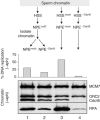
Figures

References
-
- Aparicio OM, Weinstein DM, Bell SP (1997) Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell 91: 59–69 - PubMed
-
- Avni D, Yang H, Martelli F, Hofmann F, ElShamy WM, Ganesan S, Scully R, Livingston DM (2003) Active localization of the retinoblastoma protein in chromatin and its response to S phase DNA damage. Mol Cell 12: 735–746 - PubMed
-
- Bell SP, Dutta A (2002) DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem 71: 333–374 - PubMed
-
- Blow JJ, Laskey RA (1986) Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell 47: 577–587 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

