Expression of Islet1 marks the sensory and neuronal lineages in the mammalian inner ear
- PMID: 15329890
- PMCID: PMC4158841
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.20257
Expression of Islet1 marks the sensory and neuronal lineages in the mammalian inner ear
Abstract
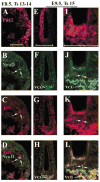
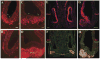
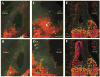
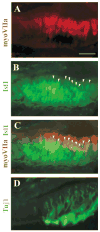
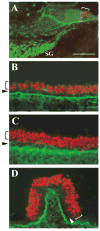
Several basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) genes have been shown to be essential for the generation of the auditory sensory hair cells or the spiral ganglion (SG) neurons that innervate the hair cells in the cochlea, as well as a variety of cell types in the other nervous systems. However, it remains elusive what cellular context-dependent mechanisms confer the inner ear-specific neuronal or sensory competency/identities. We explored the possibility that one of the mechanisms responsible for generating cellular diversity in the nervous system through cooperative action of bHLH and LIM-homeodomain (LIM-HD) transcriptional factors might also contribute to the inner ear-specific sensory and/or neuronal competency. Here, we show that Islet1 (Isl1), a LIM-HD protein, is expressed early in the otocyst in the region that gives rise to both the auditory sensory organ, the organ of Corti, and SG neurons. Subsequently, the expression of Isl1 is maintained in SG neurons but is transitory in the sensory lineage. At embryonic day 12 (E12) in mice, the expression of Isl1 marks distinctively the ventral portion of the nascent cochlear epithelium encompassing the primordial organ of Corti. At E13, Isl1 is maintained at relatively high levels in the sensory primordium while down-regulated in the other regions of the cochlear duct. As the sensory epithelium starts to differentiate, it is down-regulated in the entire cochlear epithelium. The expression of Isl1 in the developing inner ear reveals an early and likely a common step in the development of both sensory and neuronal lineages of the inner ear, and suggests its potential role in the inner ear-specific sensory and neuronal cell development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative expression analysis of POU4F1, POU4F2 and ISL1 in developing mouse cochleovestibular ganglion neurons.Gene Expr Patterns. 2014 May;15(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Gene Expr Patterns. 2014. PMID: 24709358 Free PMC article.
-
The zinc finger transcription factor Gfi1, implicated in lymphomagenesis, is required for inner ear hair cell differentiation and survival.Development. 2003 Jan;130(1):221-32. doi: 10.1242/dev.00190. Development. 2003. PMID: 12441305
-
Islet-1 expression in the developing chicken inner ear.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Sep 6;477(1):1-10. doi: 10.1002/cne.20190. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15281076
-
Atoh1 and other related key regulators in the development of auditory sensory epithelium in the mammalian inner ear: function and interplay.Dev Biol. 2019 Feb 15;446(2):133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.12.025. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30605626 Review.
-
Development and evolution of inner ear sensory epithelia and their innervation.J Neurobiol. 2002 Nov 5;53(2):143-56. doi: 10.1002/neu.10098. J Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12382272 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution transcriptional dissection of in vivo Atoh1-mediated hair cell conversion in mature cochleae identifies Isl1 as a co-reprogramming factor.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 31;14(7):e1007552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007552. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30063705 Free PMC article.
-
Pax2-Islet1 Transgenic Mice Are Hyperactive and Have Altered Cerebellar Foliation.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;54(2):1352-1368. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9716-6. Epub 2016 Feb 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26843111 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Aspects of the Development and Function of Auditory Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 24;22(1):131. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010131. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smaller inner ear sensory epithelia in Neurog 1 null mice are related to earlier hair cell cycle exit.Dev Dyn. 2005 Nov;234(3):633-50. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20551. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 16145671 Free PMC article.
-
Open chromatin dynamics in prosensory cells of the embryonic mouse cochlea.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 21;9(1):9060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45515-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31227770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam J, Myat A, Le Rous I, Eddison M, Henrique D, Horowicz D, Lewis J. Cell fate choices and the expression of Notch, Delta and Serrate homologues in the chick inner ear: parallels with Drosophila sense-organ development. Development. 1998;125:4645–4654. - PubMed
-
- Allan DW, Thor S. Together at last: bHLH and LIM-HD regulators cooperate to specify motor neurons. Neuron. 2003;38:675–677. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Arie N, Bellen HJ, Armstrong DL, McCall AE, Gordadze PR, Guo Q, Matzuk MM, Zoghbi HY. Math1 is essential for genesis of cerebellar granule neurons. Nature. 1997;390:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham NA, Hassan BA, Price SD, Vollrath MA, Ben-Arie N, Eatock RA, Bellen HJ, Lysakowski A, Zoghbi HY. Math1: an essential gene for the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science. 1999;284:1837–1841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

