WISP-1 is an osteoblastic regulator expressed during skeletal development and fracture repair
- PMID: 15331410
- PMCID: PMC1618601
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63348-2
WISP-1 is an osteoblastic regulator expressed during skeletal development and fracture repair
Abstract
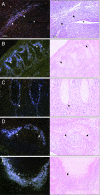
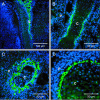
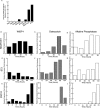
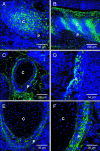
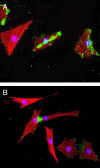
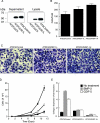
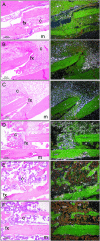
Wnt-1-induced secreted protein 1 (WISP-1) is a member of the CCN (connective tissue growth factor, Cyr61, NOV) family of growth factors. Experimental evidence suggests that CCN family members are involved in skeletogenesis and bone healing. To investigate the role of WISP-1 in osteogenic processes, we characterized its tissue and cellular expression and evaluated its activity in osteoblastic and chondrocytic cell culture models. During embryonic development, WISP-1 expression was restricted to osteoblasts and to osteoblastic progenitor cells of the perichondral mesenchyme. In vitro, we showed that WISP-1 expression in differentiating osteoblasts promotes BMP-2-induced osteoblastic differentiation. Using in situ and cell binding analysis, we demonstrated WISP-1 interaction with perichondral mesenchyme and undifferentiated chondrocytes. We evaluated the effect of WISP-1 on chondrocytes by generating stably transfected mouse chondrocytic cell lines. In these cells, WISP-1 increased proliferation and saturation density but repressed chondrocytic differentiation. Because of the similarity between skeletogenesis and bone healing, we also analyzed WISP-1 spatiotemporal expression in a fracture repair model. We found that WISP-1 expression recapitulates the pattern observed during skeletal development. Our data demonstrate that WISP-1 is an osteogenic potentiating factor promoting mesenchymal cell proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation while repressing chondrocytic differentiation. Therefore, we propose that WISP-1 plays an important regulatory role during bone development and fracture repair.
Figures
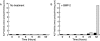
References
-
- Bork P. The modular architecture of a new family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:125–130. - PubMed
-
- Brigstock DR. The connective tissue growth factor/cysteine-rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:189–206. - PubMed
-
- Pennica D, Swanson TA, Welsh JW, Roy MA, Lawrence DA, Lee J, Brush J, Taneyhill LA, Deuel B, Lew M, Watanabe C, Cohen RL, Melhem MF, Finley GG, Quirke P, Goddard AD, Hillan KJ, Gurney AL, Botstein D, Levine AJ. WISP genes are members of the connective tissue growth factor family that are up-regulated in wnt-1-transformed cells and aberrantly expressed in human colon tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:14717–14722. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

