Cerebral expression of interleukin-12 induces neurological disease via differential pathways and recruits antigen-specific T cells in virus-infected mice
- PMID: 15331418
- PMCID: PMC1618590
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63356-1
Cerebral expression of interleukin-12 induces neurological disease via differential pathways and recruits antigen-specific T cells in virus-infected mice
Abstract
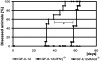
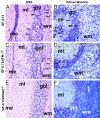
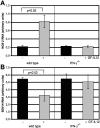
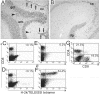
Transgenic expression of interleukin-12 (IL-12) in astrocytes causes a spontaneous inflammatory central nervous system disorder in aged mice. Here we show that spontaneous disorder developed only when both mature lymphocytes and interferon (IFN)-gamma were present. Infection with noncytolytic Borna disease virus (BDV) did not affect wild-type mice but accelerated disease of IL-12 transgenic mice. Infection of transgenic mice lacking lymphocytes did not result in neurological symptoms. In contrast, BDV infection of transgenic mice lacking IFN-gamma induced neurological disease with delayed onset of symptoms that resembled those in infected transgenic mice with a functional IFN-gamma gene. In BDV-infected transgenic mice devoid of IFN-gamma no cerebellar calcification was observed, and multiplication of BDV was not inhibited. To determine the antigen specificity of lymphocytes in brains of diseased animals, the IL-12 transgene was introduced into an H-2k genetic background. Infection of IL-12 transgenic H-2k mice resulted in extensive lymphocytic infiltration into the cerebellum but not into other brain regions that also contained viral antigen but expressed the transgene at lower levels. Tetramer analysis revealed that most CD8 T cells in the cerebellum of such mice were BDV-specific. Our results thus demonstrate that IFN-gamma secreting lymphocytes are responsible for disease of IL-12 transgenic mice. They further suggest that expression of IL-12 in the central nervous system may lead to localized recruitment of T cells that recognize antigens expressed in the brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The functional avidity of virus-specific CD8+ T cells is down-modulated in Borna disease virus-induced immunopathology of the central nervous system.Eur J Immunol. 2005 Feb;35(2):487-97. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425232. Eur J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15627979
-
Antiviral CD8 T cells recognize borna disease virus antigen transgenically expressed in either neurons or astrocytes.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):3099-108. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02479-07. Epub 2008 Jan 9. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18184705 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic potential of borna disease virus lacking the immunodominant CD8 T-cell epitope.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11187-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00742-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17686872 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma prevents death of bystander neurons during CD8 T cell responses in the brain.Am J Pathol. 2009 May;174(5):1799-807. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080897. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19359516 Free PMC article.
-
Brain cell lesions in Borna disease are mediated by T cells.Arch Virol Suppl. 1993;7:153-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9300-6_12. Arch Virol Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8219800 Review.
Cited by
-
Trafficking of immune cells in the central nervous system.J Clin Invest. 2010 May;120(5):1368-79. doi: 10.1172/JCI41911. Epub 2010 May 3. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20440079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid treatment of MCMV infected newborn mice attenuates CNS inflammation and limits deficits in cerebellar development.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Mar;9(3):e1003200. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003200. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23505367 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles for CXCR3 signaling in central nervous system versus ocular inflammation mediated by the astrocyte-targeted production of IL-12.Am J Pathol. 2011 Nov;179(5):2346-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.041. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21925471 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of an astrocyte-derived inflammatory protein, S100B, reduces vascular inflammatory responses in brains persistently infected with Borna disease virus.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5940-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02137-06. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17376896 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-overexpression in Borna disease virus-infected mouse brains triggers inflammatory reaction and epileptic seizures.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041476. Epub 2012 Jul 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and its role in the generation of TH1 cells. Immunol Today. 1993;14:335–338. - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a cytokine at the interface of inflammation and immunity. Adv Immunol. 1998;70:83–243. - PubMed
-
- Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN. Inflammatory cytokines within the central nervous system: sources, function, and mechanism of action. Am J Physiol. 1992;263:C1–C16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

