Rational design of DNA sequences for nanotechnology, microarrays and molecular computers using Eulerian graphs
- PMID: 15333695
- PMCID: PMC516071
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh802
Rational design of DNA sequences for nanotechnology, microarrays and molecular computers using Eulerian graphs
Abstract
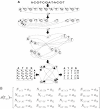
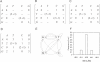
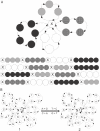
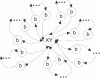
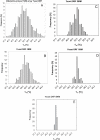
Nucleic acids are molecules of choice for both established and emerging nanoscale technologies. These technologies benefit from large functional densities of 'DNA processing elements' that can be readily manufactured. To achieve the desired functionality, polynucleotide sequences are currently designed by a process that involves tedious and laborious filtering of potential candidates against a series of requirements and parameters. Here, we present a complete novel methodology for the rapid rational design of large sets of DNA sequences. This method allows for the direct implementation of very complex and detailed requirements for the generated sequences, thus avoiding 'brute force' filtering. At the same time, these sequences have narrow distributions of melting temperatures. The molecular part of the design process can be done without computer assistance, using an efficient 'human engineering' approach by drawing a single blueprint graph that represents all generated sequences. Moreover, the method eliminates the necessity for extensive thermodynamic calculations. Melting temperature can be calculated only once (or not at all). In addition, the isostability of the sequences is independent of the selection of a particular set of thermodynamic parameters. Applications are presented for DNA sequence designs for microarrays, universal microarray zip sequences and electron transfer experiments.
Figures

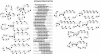
Similar articles
-
Selection of long oligonucleotides for gene expression microarrays using weighted rank-sum strategy.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Sep 19;8:350. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-350. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17880708 Free PMC article.
-
Individual sequences in large sets of gene sequences may be distinguished efficiently by combinations of shared sub-sequences.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 8;6:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-90. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15817134 Free PMC article.
-
Solving satisfiability problems using a novel microarray-based DNA computer.Biosystems. 2007 Jul-Aug;90(1):242-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2006.08.009. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Biosystems. 2007. PMID: 17029765
-
Cluster analysis and promoter modelling as bioinformatics tools for the identification of target genes from expression array data.Pharmacogenomics. 2001 Feb;2(1):25-36. doi: 10.1517/14622416.2.1.25. Pharmacogenomics. 2001. PMID: 11258194 Review.
-
Microarray: an approach for current drug targets.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 Mar;9(3):221-31. doi: 10.2174/138920008783884795. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18336225 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and contextual markers of hepatitis C virus and drug abuse.Mol Diagn Ther. 2009;13(3):153-79. doi: 10.2165/01250444-200913030-00002. Mol Diagn Ther. 2009. PMID: 19650670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of locked nucleic acid residues on the thermodynamic properties of 2'-O-methyl RNA/RNA heteroduplexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Sep 9;33(16):5082-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki789. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16155181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benight A.S., Pancoska,P., Owczarzy,R., Vallone,P.M., Nesetril,J. and Riccelli,P.V. (2001) Calculating sequence-dependent melting stability of duplex DNA oligomers and multiplex sequence analysis by graphs. Methods Enzymol., 340, 165–192. - PubMed
-
- SantaLucia J. Jr, Kierzek,R. and Turner,D.H. (1991) Stabilities of consecutive A.C, C.C, G.G, U.C, and U.U mismatches in RNA internal loops: evidence for stable hydrogen-bonded U.U and C.C.+ pairs. Biochemistry, 30, 8242–8251. - PubMed
-
- SantaLucia J. Jr, Allawi,H.T. and Seneviratne,P.A. (1996) Improved nearest-neighbor parameters for predicting DNA duplex stability. Biochemistry, 35, 3555–3562. - PubMed
-
- Xia T., SantaLucia,J.,Jr, Burkard,M.E., Kierzek,R., Schroeder,S.J., Jiao,X., Cox,C. and Turner,D.H. (1998) Thermodynamic parameters for an expanded nearest-neighbor model for formation of RNA duplexes with Watson–Crick base pairs. Biochemistry, 37, 14719–14735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

