Expression of toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 gene and protein in Kupffer cells after ischemia-reperfusion in rat liver graft
- PMID: 15334694
- PMCID: PMC4572126
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2890
Expression of toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 gene and protein in Kupffer cells after ischemia-reperfusion in rat liver graft
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and MD-2 gene and protein in Kupffer cells (KCs) and their role in ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury of rat liver graft.
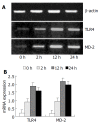
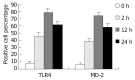
Methods: KCs were isolated at 0 (control group), 2, 12, 24 h (IR group) following IR in rat liver graft. mRNA expression of TLR4 and MD-2 was detected by RT-PCR analysis, protein expression of TLR4/MD-2 was detected by flow cytometric (FCM) analysis, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) level in supernatant was measured by ELISA. Then isolated KCs were incubated with anti-TLR4 polyclonal antibody (anti-TLR4 group), and TNF-alpha level was measured again.
Results: The mRNA and protein expression of TLR4/MD-2 and the level of TNF-alpha in IR group increased significantly at 2 h following IR, and reached the maximum at 12 h, and slightly decreased at 24 h, but were still significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.01). The expression of these factors was markedly decreased after anti-TLR4 antibody treatment as compared with the IR group (P<0.01).
Conclusion: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) following IR can up-regulate TLR4/MD-2 gene and protein expression in KCs, and synthesize cytokine TNF-alpha. Anti TLR4 antibody can inhibit the production of TNF-alpha induced by LPS. TLR4 and its partner molecule MD-2 may play an important role in Kupffer cell activation and IR injury.
Figures

References
-
- Latz E, Visintin A, Lien E, Fitzgerald KA, Espevik T, Golenbock DT. The LPS receptor generates inflammatory signals from the cell surface. J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9:375–380. - PubMed
-
- Espevik T, Latz E, Lien E, Monks B, Golenbock DT. Cell distributions and functions of Toll-like receptor 4 studied by fluorescent gene constructs. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35:660–664. - PubMed
-
- Kimoto M, Nagasawa K, Miyake K. Role of TLR4/MD-2 and RP105/MD-1 in innate recognition of lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35:568–572. - PubMed
-
- Harada K, Ohira S, Isse K, Ozaki S, Zen Y, Sato Y, Nakanuma Y. Lipopolysaccharide activates nuclear factor-kappaB through toll-like receptors and related molecules in cultured biliary epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 2003;83:1657–1667. - PubMed
-
- Fujihara M, Muroi M, Tanamoto K, Suzuki T, Azuma H, Ikeda H. Molecular mechanisms of macrophage activation and deactivation by lipopolysaccharide: roles of the receptor complex. Pharmacol Ther. 2003;100:171–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

