Membrane insertion of anthrax protective antigen and cytoplasmic delivery of lethal factor occur at different stages of the endocytic pathway
- PMID: 15337774
- PMCID: PMC2172425
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200312072
Membrane insertion of anthrax protective antigen and cytoplasmic delivery of lethal factor occur at different stages of the endocytic pathway
Abstract
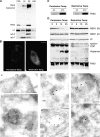
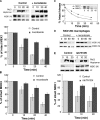
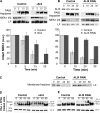
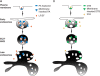
The protective antigen (PA) of anthrax toxin binds to a cell surface receptor, undergoes heptamerization, and binds the enzymatic subunits, the lethal factor (LF) and the edema factor (EF). The resulting complex is then endocytosed. Via mechanisms that depend on the vacuolar ATPase and require membrane insertion of PA, LF and EF are ultimately delivered to the cytoplasm where their targets reside. Here, we show that membrane insertion of PA already occurs in early endosomes, possibly only in the multivesicular regions, but that subsequent delivery of LF to the cytoplasm occurs preferentially later in the endocytic pathway and relies on the dynamics of internal vesicles of multivesicular late endosomes.
Figures

References
-
- Abrami, L., M. Fivaz, E. Decroly, N.G. Seidah, J. François, G. Thomas, S. Leppla, J.T. Buckley, and F.G. van der Goot. 1998. The pore-forming toxin proaerolysin is processed by furin. J. Biol. Chem. 273:32656–32661. - PubMed
-
- Chow, A., D. Toomre, W. Garrett, and I. Mellman. 2002. Dendritic cell maturation triggers retrograde MHC class II transport from lysosomes to the plasma membrane. Nature. 418:988–994. - PubMed
-
- Collier, R.J., and J.A. Young. 2003. Anthrax toxin. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19:45–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

