Alternative splicing of Drosophila Dscam generates axon guidance receptors that exhibit isoform-specific homophilic binding
- PMID: 15339666
- PMCID: PMC2691713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.021
Alternative splicing of Drosophila Dscam generates axon guidance receptors that exhibit isoform-specific homophilic binding
Abstract
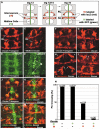
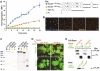
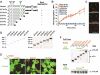
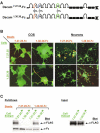
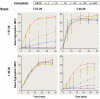
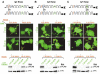
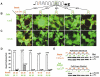
Dscam is an immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily protein required for the formation of neuronal connections in Drosophila. Through alternative splicing, Dscam potentially gives rise to 19,008 different extracellular domains linked to one of two alternative transmembrane segments, resulting in 38,016 isoforms. All isoforms share the same domain structure but contain variable amino acid sequences within three Ig domains in the extracellular region. We demonstrate that different isoforms exhibit different binding specificity. Each isoform binds to itself but does not bind or binds poorly to other isoforms. The amino acid sequences of all three variable Ig domains determine binding specificity. Even closely related isoforms sharing nearly identical amino acid sequences exhibit isoform-specific binding. We propose that this preferential homophilic binding specificity regulates interactions between cells and contributes to the formation of complex patterns of neuronal connections.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwala KL, Nakamura S, Tsutsumi Y, Yamakawa K. Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule DSCAM mediates homophilic intercellular adhesion. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000;79:118–126. - PubMed
-
- Agarwala KL, Ganesh S, Tsutsumi Y, Suzuki T, Amano K, Yamakawa K. Cloning and functional characterization of DSCAML1, a novel DSCAM-like cell adhesion molecule that mediates homophilic intercellular adhesion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001;285:760–772. - PubMed
-
- Clemens JC, Ursuliak Z, Clemens KK, Price JV, Dixon J. A Drosophila protein-tyrosine phosphatase associates with an adapter protein required for axonal guidance. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:17002–17005. - PubMed
-
- Feinstein P, Mombaerts P. A contextual model for axonal sorting into glomeruli in the mouse olfactory system. Cell. 2004;117:817–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

