Electroosmosis in transdermal iontophoresis: implications for noninvasive and calibration-free glucose monitoring
- PMID: 15339817
- PMCID: PMC1304802
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.044792
Electroosmosis in transdermal iontophoresis: implications for noninvasive and calibration-free glucose monitoring
Abstract
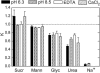
Reverse iontophoresis uses a small low electric current to noninvasively extract blood analytes, e.g., glucose, across the skin. The simultaneous quantification of the analyte extracted and of an additional endogenous substance of fixed and known concentration in the body permits the blood level of interest to be found without the need for an invasive calibration procedure. The transport phenomena underlying this approach, applied to glucose monitoring, has been investigated in vitro, using Na+ and neutral model solutes as endogenous "internal standards" (specifically, urea, glycerol, mannitol, and sucrose). The cathodal extracted fluxes of glucose under conditions of modified skin permselectivity were related to those of the different, potential internal standards. Flux ratios depended upon the iontophoretic conditions and the size of the neutral internal standards, whereas high variability was observed with Na+. Constant flux ratios were obtained with mannitol, glycerol, urea, and sucrose for which the mechanism of electrotransport was identical to that of glucose. The advantage of using a neutral internal standard, however, must be weighed against the need to identify and validate the marker under physiological conditions and the additional analytical chemistry necessary for the practical quantification of this substance.
Figures
References
-
- Bankir, L., and M. M. Trinh-Trang-Tan. 2000. Urea and the kidney. In The Kidney. B. M. Brenner, editor. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA. 637–679.
-
- Burnette, R. R., and B. Ongpipattanakul. 1987. Characterization of the permselective properties of excised human skin during iontophoresis. J. Pharm. Sci. 76:765–773. - PubMed
-
- Delgado-Charro, M. B., and R. H. Guy. 2003. Transdermal reverse iontophoresis of valproate: a non-invasive method for therapeutic drug monitoring. Pharm. Res. 20:1508–1513. - PubMed
-
- Glikfeld, P., R. S. Hinz, and R. H. Guy. 1989. Noninvasive sampling of biological fluids by iontophoresis. Pharm. Res. 6:988–990. - PubMed
-
- Guy, R. H., Y. N. Kalia, M. B. Delgado-Charro, V. Merino, A. Lopez, and D. Marro. 2000. Iontophoresis: electrorepulsion and electroosmosis. J. Control. Release. 64:129–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical